Expanding the Application of Sentinel-2 Chlorophyll Monitoring across United States Lakes
- PMID: 38994037
- PMCID: PMC11235139
- DOI: 10.3390/rs16111977
Expanding the Application of Sentinel-2 Chlorophyll Monitoring across United States Lakes
Abstract
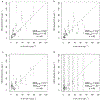
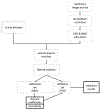
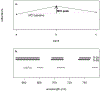
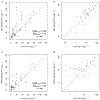
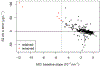
Eutrophication of inland lakes poses various societal and ecological threats, making water quality monitoring crucial. Satellites provide a comprehensive and cost-effective supplement to traditional in situ sampling. The Sentinel-2 MultiSpectral Instrument (S2 MSI) offers unique spectral bands positioned to quantify chlorophyll a, a water-quality and trophic-state indicator, along with fine spatial resolution, enabling the monitoring of small waterbodies. In this study, two algorithms-the Maximum Chlorophyll Index (MCI) and the Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index (NDCI)-were applied to S2 MSI data. They were calibrated and validated using in situ chlorophyll a measurements for 103 lakes across the contiguous U.S. Both algorithms were tested using top-of-atmosphere reflectances (ρ t), Rayleigh-corrected reflectances (ρ s), and remote sensing reflectances (R rs ). MCI slightly outperformed NDCI across all reflectance products. MCI using ρ t showed the best overall performance, with a mean absolute error factor of 2.08 and a mean bias factor of 1.15. Conversion of derived chlorophyll a to trophic state improved the potential for management applications, with 82% accuracy using a binary classification. We report algorithm-to-chlorophyll-a conversions that show potential for application across the U.S., demonstrating that S2 can serve as a monitoring tool for inland lakes across broad spatial scales.
Keywords: Sentinel-2; chlorophyll a; eutrophication; lakes; remote sensing; water quality monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author N.P. was employed by the company Science Systems and Applications, Inc. Author M.M.C. was employed by the company Global Science & Technology, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results..
Figures



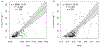



References
-
- Conley DJ; Paerl HW; Howarth RW; Boesch DF; Seitzinger SP; Havens KE; Lancelot C; Likens GE Controlling Eutrophication: Nitrogen and Phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. - PubMed
-
- Smith VH; Joye SB; Howarth RW Eutrophication of freshwater and marine systems. Limnol. Oceanogr 2006, 51, 351–355.
-
- Mishra P; Naik S; Babu PV; Pradhan U; Begum M; Kaviarasan T; Vashi A; Bandyopadhyay D; Ezhilarasan P; Panda US; et al. Algal bloom, hypoxia, and mass fish kill events in the backwaters of Puducherry, Southeast coast of India. Oceanologia 2022, 64, 396–403.
-
- Sivonen K Cyanobacterial toxins and toxin production. Phycologia 1996, 35, 12–24.
-
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Safe Recreational Water Environments. Volume 1: Coastal and Fresh Waters; Chapter 8: Algae and Cyanobacteria in Fresh Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
