Unlocking the biological potential of transition metal complexes with Thiosemicarbazone ligands: Insights from computational studies
- PMID: 38994046
- PMCID: PMC11238129
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33150
Unlocking the biological potential of transition metal complexes with Thiosemicarbazone ligands: Insights from computational studies
Abstract
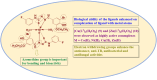
In the previous study, the synthesis and characterization of 4-(3-fluorophenyl)-3-thiosemicarbazide and benzaldehyde derivatives based thiosemicarbazone ligands and their Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) complexes were carried out to evaluate their malarial and oxidant and inflammatory inhibition abilities, demonstrating that these compounds have robust efficacy for these ailments. In the present research, to find out a combating agent against breast cancer, tuberculosis, bacterial and fungal ailments, the compounds were tested through MTT, microplate alamar blue and serial dilution protocols. ADMET and DFT investigation were analyzed against highly bioactive compounds (2, 7-10) to give a new insight about compound's reactivity, stability and drug likeness properties. Furthermore, activity results shows that the ligand (2) and its complexes demonstrate greater efficacy compared to ligand (1) and its complexes. The Cu(II) (9) and Zn(II) (10) complexes were observed as highly efficient for breast cancer (MCF-7 cell line), TB (H37Rv strain), bacterial and fungal ailments in comparison of standard drugs with 0.029 ± 0.001 μM IC50 value for (9) in anticancer activity and 0.0034 ± 0.0017 μmol/mL MIC value for (10) in anti-tuberculosis activity. In the molecular docking investigation, the various kind of binding interactions and lowest binding affinity of (9) (against 4RJ3 (-10.0 kcal/mol), 2VCJ (-7.9 kcal/mol)) and (10) (-7.8 and -8.3 kcal/mol for 5V3Y and 3PTY protein) support their bioactivity. This research highlights the pharmaceutical importance of transition metal complexes having thiosemicarbazones, presenting a significant approach for the discovery of potent anti-infectious agent.
Keywords: ADMET; Anti-tuberculosis; Anticancer; Molecular docking; Transition metal.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computer-aided drug design and virtual screening of targeted combinatorial libraries of mixed-ligand transition metal complexes of 2-butanone thiosemicarbazone.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Aug;75:178-195. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.05.008. Epub 2018 May 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29883916
-
Biological and Computational Studies of Hydrazone Based Transition Metal(II) Complexes.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Nov;21(11):e202401116. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401116. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 39039909
-
Synthesis, characterization, thermal properties, antimicrobial evaluation, ADMET study, and molecular docking simulation of new mono Cu (II) and Zn (II) complexes with 2-oxoindole derivatives.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jun;145:105473. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105473. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35395516
-
Molecular docking, PASS analysis, bioactivity score prediction, synthesis, characterization and biological activity evaluation of a functionalized 2-butanone thiosemicarbazone ligand and its complexes.J Chem Biol. 2017 Apr 4;10(3):91-104. doi: 10.1007/s12154-017-0167-y. eCollection 2017 Jul. J Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 28684996 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, computational studies and biological activity evaluation of Cu, Fe, Co and Zn complexes with 2-butanone thiosemicarbazone and 1,10-phenanthroline ligands as anticancer and antibacterial agents.EXCLI J. 2018 Mar 29;17:331-348. doi: 10.17179/excli2017-984. eCollection 2018. EXCLI J. 2018. PMID: 29743867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploration of newly synthesized transition metal(II) complexes for infectious diseases.Future Med Chem. 2024;16(20):2087-2105. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2389766. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Future Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39295510
References
-
- Yousef T.A., El-Reash G.A. Synthesis, and biological evaluation of complexes based on thiosemicarbazone ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 2020;1201 doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127180. - DOI
-
- Netalkar P.P., Netalkar S.P., Revankar V.K. Transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazone: synthesis, structures and invitro antimicrobial studies. Polyhedron. 2015;100:215–222. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2015.07.075. - DOI
-
- Rani S., Sumrra S.H., Chohan Z.H. Metal based sulfanilamides: a note on their synthesis, spectral characterization, and antimicrobial activity. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017;87:1834–1842. doi: 10.1134/S107036321708031X. - DOI
-
- Devi J., Kumar B., Taxak B. Recent advancements of organotin (IV) complexes derived from hydrazone and thiosemicarbazone ligands as potential anticancer agents. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022;139 doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109208. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

