Relationships between social networking sites use and subjective well-being--- a meta-analysis and meta-analytic structural equation model
- PMID: 38994060
- PMCID: PMC11237853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32463
Relationships between social networking sites use and subjective well-being--- a meta-analysis and meta-analytic structural equation model
Abstract
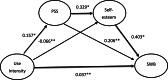
During the last decade, the amount of research on the relationship between social networking sites (SNS) use and users' subjective well-being (SWB) has increased, leading to discrepancies regarding the results. Our review of the literature generated 73 independent samples and indicated that considerable inconsistent results may be attributed to different measurements of SNS use, moderation effects, or media response states and their effects. In this study, meta-analytic procedures were used to assess the strength of the relationships between SNS use indicators, perceived social support (PSS), self-esteem and SWB. The results showed that PSS and self-esteem had stronger effects on SWB than SNS use indicators. Furthermore, a meta-analytic structural equation model was conducted to assess the strength of the relationships between SNS use indicators, PSS, self-esteem, and SWB. The results did not support the proposition SNS use is associated with SWB. Compared with SNS use indicators, media response states such as self-esteem and PSS, had more effects on SWB.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Meta-analytic structural equation model; Perceived social support; Self-esteem; Social networking site; Subjective well-being.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Qiuhong Yang reports financial support was provided by Jiangsu Education Department [Grant No. 2020SJA1602]. Ying Feng reports financial support was provided by National Social Science Found of China[Grant No. 20BTQ047].
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Mediating Roles of Upward Social Comparison and Self-esteem and the Moderating Role of Social Comparison Orientation in the Association between Social Networking Site Usage and Subjective Well-Being.Front Psychol. 2017 May 11;8:771. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00771. eCollection 2017. Front Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28553256 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the use of social networking sites, perceived social support, and life satisfaction: Evidence from a population-based survey in Japan.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 18;15(12):e0244199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244199. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33338072 Free PMC article.
-
Social Networking Site Use While Driving: ADHD and the Mediating Roles of Stress, Self-Esteem and Craving.Front Psychol. 2016 Mar 30;7:455. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00455. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27065923 Free PMC article.
-
Social comparison on social networking sites.Curr Opin Psychol. 2020 Dec;36:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2020.04.002. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Curr Opin Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32387840 Review.
-
Social Networking Site Use and Loneliness: A Meta-Analysis.J Psychol. 2022;156(7):492-511. doi: 10.1080/00223980.2022.2101420. Epub 2022 Aug 18. J Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35981234 Review.
References
-
- Kaplan A.M., Haenlein M. Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Bus. Horiz. 2010 Jan;53(1):59–68.
-
- Tankovska H. Average daily time spent on social networks in the U.S. 2018-2022. 2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1018324/us-users-daily-social-media-...
-
- Boyd D., Ellison N.B. Social network sites: definition, history, and scholarship. J. Computer-Mediated Commun. 2007 Oct;13(1):210–230.
-
- Kemp E. Global social media statistics. 2022. https://datareportal.com/social-media-users
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

