Epigenetic silencing of miR-125a-3p promotes the progress of human cholangiocarcinoma via increasing CAC1 expression
- PMID: 38994075
- PMCID: PMC11237926
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32528
Epigenetic silencing of miR-125a-3p promotes the progress of human cholangiocarcinoma via increasing CAC1 expression
Abstract
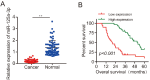
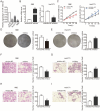
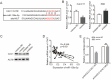
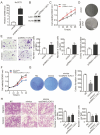
We aimed to investigate the dysregulation of the microRNAs(miRNAs) in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), including its impact on the homeostasis of the transcriptome and cellular behavior. MiRNAs serve as potent epigenetic regulators of transcriptional output, targeting various signaling pathways. This study aimed to investigate the expression level, epigenetic mechanism and function of miR-125a-3 in CCA. The study data showed that the expression level of miR125a-3p was decreased in CCA tissue samples and cell lines, and it was closely related to lymph node metastasis, tissue differentiation and TNM stage. The data demonstrate a strong association between decreased miR-125a-3p expression and poorer prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma patients. miR-125a-3p acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting the viability, migration and invasion of CCA cells. There are CpG islands in the promoter region of miR-125a-3p gene, and the methylation of the promoter region of miR-125a-3p gene leads to the transcriptional repression of miR-125a-3p. In addition, miR125a-3p can target and regulate CAC1 mRNA and protein expression in the downstream mechanism, and the high expression of CAC1 can promote the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells. These data demonstrate that miR-125a-3p promoter methylation leads to silencing of its expression. Mechanically, miR-125a-3p acts as a tumor suppressor and participates in the occurrence and development of CCA through targeting CAC1 gene expression. Therefore, miR-125a-3p may serve as a new target for the diagnosis, prognostic assessment or molecular therapy of CCA.
Keywords: CAC1; Cholangiocarcinoma; Malignant progression; Methylation; miR-125a-3p; microRNA.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Lamarca A., Santos-Laso A., Utpatel K., La Casta A., Stock S., Forner A., Adeva J., Folseraas T., Fabris L., Macias R.I.R., Krawczyk M., Krawczyk M., Cardinale V., Braconi C., Alvaro D., Evert M., Banales J.M., Valle J.W., Group: on behalf of the European Network for the Study of C Liver metastases of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: implications for an updated staging system. Hepatology. 2021;73:2311–2325. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nara S., Esaki M., Ban D., Takamoto T., Shimada K., Ioka T., Okusaka T., Ishii H., Furuse J. Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy for biliary tract cancer: a review of clinical trials. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;50:1353–1363. - PubMed
-
- Tummanatsakun D., Proungvitaya T., Roytrakul S., Limpaiboon T., Wongkham S., Wongkham C., Silsirivanit A., Somintara O., Sangkhamanon S., Proungvitaya S. Serum apurinic/apyrimidinic endodeoxyribonuclease 1 (APEX1) level as a potential biomarker of cholangiocarcinoma. Biomolecules. 2019;9 - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

