Development of a simple and highly sensitive virion concentration method to detect SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
- PMID: 38994082
- PMCID: PMC11238118
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33168
Development of a simple and highly sensitive virion concentration method to detect SARS-CoV-2 in saliva
Abstract
Background: Controlling novel coronavirus pandemic infection (COVID-19) is a global challenge, and highly sensitive testing is essential for effective control. The saliva is a promising sample for high-sensitivity testing because it is easier to collect than nasopharyngeal swab samples and allows large-volume testing.
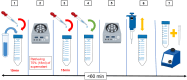
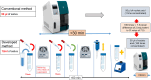
Results: We developed a simple SARS-CoV-2 concentration method from saliva samples that can be completed in less than 60 min. We performed a spike test using 12 ml of saliva samples obtained from healthy volunteer people, and the developed method performance was evaluated by comparison using a combination of automatic nucleic acid extraction followed by RT-qPCR detection. In saliva spike tests using a 10-fold dilution series of SARS-CoV-2, the developed method was consistently 100-fold more sensitive than the conventional method.
Conclusions: The developed method can improve the analytical sensitivity of the SARS-CoV-2 test using saliva and speed up and save labor in screening tests by pooling many samples. Furthermore, the developed method has the potential to contribute to the highly sensitive detection of various human and animal viral pathogens from the saliva and various clinical samples.
Keywords: COVID-19; Concentration; SARS-CoV-2; Semi alkaline proteinase; Virion; Virus.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Saliva as a testing specimen with or without pooling for SARS-CoV-2 detection by multiplex RT-PCR test.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 23;16(2):e0243183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243183. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33621263 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Saliva-Based RNA Extraction-Free One-Step Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Mass SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring.Molecules. 2021 Oct 31;26(21):6617. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216617. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34771026 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a point-of-care test to detect SARS-CoV-2 from saliva which combines a simple RNA extraction method with colorimetric reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification detection.J Clin Virol. 2021 Mar;136:104760. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104760. Epub 2021 Feb 11. J Clin Virol. 2021. PMID: 33610926 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-Based Detection Using Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens in Asymptomatic Populations.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Sep 3;9(1):e0006221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00062-21. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34431689 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A highly sensitive method for detecting African swine fever virus in oral fluids from naturally infected pigs in Northern Vietnam.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 30;15(1):27855. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12139-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40739285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan J.F., Yip C.C., To K.K., et al. Improved molecular diagnosis of COVID-19 by the novel, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay validated in vitro and with clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58(5):e00310–e00320. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00310-20. Published 2020 Apr 23. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

