Impacts of designed vanillic acid-polymer-magnetic iron oxide nanocomposite on breast cancer cells
- PMID: 38994094
- PMCID: PMC11237972
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32863
Impacts of designed vanillic acid-polymer-magnetic iron oxide nanocomposite on breast cancer cells
Abstract
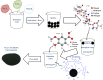
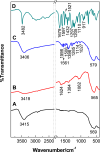
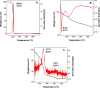
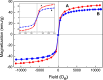
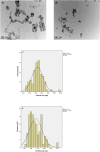
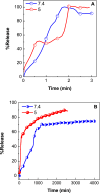
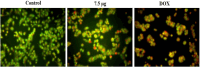
The engineered nano-vehicle was constructed using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONs) and chitosan (CTS) to stabilize anticancer agent vanillic acid (VNA) which was loaded on CTS-coated MIONs nanocarrier, and more importantly, to achieve sustained VNA release and subsequent proper anticancer activity. The new thermally stable VNA-CTS- MIONs nanocomposite was spherical with a middle diameter of 6 nm and had a high drug loading of about 11.8 %. The MIONs and resulting nanocomposite were composed of pure magnetite and therefore, were superparamagnetic with saturation magnetizations of 53.3 and 45.7 emu.g-1, respectively. The release profiles of VNA from VNA-CTS-MIONs nanocomposite in different pH values were sustained and showed controlled pH-responsive delivery of the loaded VNA with 89 % and 74 % percentage release within 2354 and 4046 min at pH 5 and 7.4, respectively, as well as were in accordance with the pseudo-second-order model. The VNA-CTS-MIONs nanocomposite treatment at diverse concentrations remarkably decreased the viability and promoted ROS accumulation and apoptosis in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Hence, it can be a propitious candidate for the management of breast cancer in the future.
Keywords: Anticancer nano-delivery; Breast cancer; Chitosan; Nanocomposite; Vanillic acid.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Dewangan J., Tandon D., Srivastava S., Verma A.K., Yapuri A., Rath S.K. Novel combination of salinomycin and resveratrol synergistically enhances the antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects on human breast cancer cells. Apoptosis. 2017;22:1246–1259. - PubMed
-
- Passos J.S., Dartora V.F.M.C., Salata G.C., Malago I.D., Lopes L.B. Contributions of nanotechnology to the intraductal drug delivery for local treatment and prevention of breast cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2023;635 - PubMed
-
- Elumalai K., Srinivasan S., Shanmugam A. Review of the efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for cancer treatment, Biomed. Technol. 2024;5:109–122.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

