Prediction and assessment of deleterious and disease causing nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in human FOXP4 gene: An in - silico study
- PMID: 38994097
- PMCID: PMC11237951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32791
Prediction and assessment of deleterious and disease causing nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in human FOXP4 gene: An in - silico study
Abstract
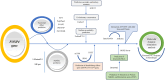
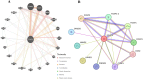
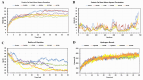
In humans, FOXP gene family is involved in embryonic development and cancer progression. The FOXP4 (Forkhead box protein P4) gene belongs to this FOXP gene family. FOXP4 gene plays a crucial role in oncogenesis. Single nucleotide polymorphisms are biological markers and common determinants of human diseases. Mutations can largely affect the function of the corresponding protein. Therefore, the molecular mechanism of nsSNPs in the FOXP4 gene needs to be elucidated. Initially, the SNPs of the FOXP4 gene were extracted from the dbSNP database and a total of 23124 SNPs was found, where 555 nonsynonymous, 20525 intronic, 1114 noncoding transcript, 334 synonymous were obtained and the rest were unspecified. Then, a series of bioinformatics tools (SIFT, PolyPhen2, SNAP2, PhD SNP, PANTHER, I-Mutant2.0, MUpro, GOR IV, ConSurf, NetSurfP 2.0, HOPE, DynaMut2, GeneMANIA, STRING and Schrodinger) were used to explore the effect of nsSNPs on FOXP4 protein function and structural stability. First, 555 nsSNPs were analyzed using SIFT, of which 57 were found as deleterious. Following, PolyPhen2, SNAP2, PhD SNP and PANTHER analyses, 10 nsSNPs (rs372762294, rs141899153, rs142575732, rs376938850, rs367607523, rs112517943, rs140387832, rs373949416, rs373949416 and rs376160648) were common and observed as deleterious, damaging and diseases associated. Following that, using I-Mutant2.0 and MUpro servers, 7 nsSNPs were found to be the most unstable. GOR IV predicted that these seven nsSNPs affect protein structure by altering the protein contents of alpha helixes, extended strands, and random coils. Following DynaMut2, 5 nsSNPs showed a decrease in the ΔΔG value compared with the wild-type and were found to be responsible for destabilizing the corresponding protein. GeneMANIA and STRING network revealed interaction of FOXP4 with other genes. Finally, molecular dynamics simulation analysis revealed consistent fluctuation in RMSD and RMSF values, Rg and hydrogen bonds in the mutant proteins compared with WT, which might alter the functional and structural stability of the corresponding protein. As a result, the aforementioned integrated comprehensive bioinformatic analyses provide insight into how various nsSNPs of the FOXP4 gene change the structural and functional properties of the corresponding protein, potentially proceeding with the pathophysiology of human diseases.
Keywords: FOXP4 gene; Functional prediction; Secondary and tertiary structure and interaction analysis; Stability prediction.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Liu M., Shi X., Wang J., Xu Y., Wei D., Zhang Y., Yang K., Wang X., Liang S., Chen X., Yang F., Sun L., Zhu X., Zhao C., Zhu L., Tang L., Zheng C., Yang Z. Association of FOXP4 gene with prostate cancer and the cumulative effects of rs4714476 and 8q24 in Chinese men. Clin. Lab. 2015;10 doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2015.150313. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

