Role of Sirolimus and Rituximab in the Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis
- PMID: 38994192
- PMCID: PMC11239162
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001414
Role of Sirolimus and Rituximab in the Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Abstract
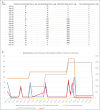
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a rare chronic liver disease affecting annually 100,000-200,000 individuals in the United States. The first-line therapy in AIH is azathioprine and corticosteroids. However, adverse events may occur, which can preclude disease remission. In these cases, mycophenolate, mercaptopurine, and tacrolimus can be used. Rituximab is offered in difficult to treat cases. Sirolimus is an alternative regimen. However, little is known about its use in AIH. This is a challenging case of "difficult to treat" AIH managed with sirolimus and rituximab, after multiple unsuccessful trials with other medications.
Keywords: autoimmune hepatitis; autoimmune liver disease; liver; rituximab; sirolimus.
© 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Figures
References
-
- Linzay CD, Sharma B, Pandit S. Autoimmune Hepatitis. StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, 2023. - PubMed
-
- Heneghan MA, McFarlane IG. Current and novel immunosuppressive therapy for autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology. 2002;35(1):7–13. - PubMed
-
- Chatrath H, Allen L, Boyer TD. Use of sirolimus in the treatment of refractory autoimmune hepatitis. Am J Med. 2014;127(11):1128–31. - PubMed
-
- Pape S Snijders R Gevers TJG, et al. . Systematic review of response criteria and endpoints in autoimmune hepatitis by the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. J Hepatol. 2022;76(4):841–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

