Prognostic role of the stromal cell derived factor-1 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
- PMID: 38994298
- PMCID: PMC11235443
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3845
Prognostic role of the stromal cell derived factor-1 in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
Abstract
Background: Stromal cell derived factor-1 (SDF-1) plays a pivotal role in the recruitment of stem cells to injured livers. However, the changes of SDF-l in patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) have yet to be elucidated.
Aim: To study the SDF-1 changes in patients with HBV-related ACLF.
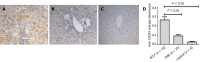
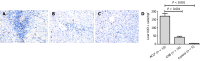
Methods: 30 patients with HBV-related ACLF, 27 patients with chronic hepatitis B and 20 healthy individuals are involved in our study. The SDF-l mRNA expression in liver tissue was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to illustrate the expression of SDF-l, CXC receptor 4 (CXCR4) and Ki67. The serum SDF-l concentrations were also detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
Results: The expression of SDF-1 mRNA from ACLF patients was remarkably higher than that from other patients (both P < 0.05). The expression of SDF-l, CXCR4 and Ki67 from ACLF were the highest among the three groups (all P < 0.01). The serum SDF-l levels in ACLF patients were significantly lower than that in other patients (both P < 0.01). Moreover, in ACLF patients, the serum SDF-1 Levels were positively correlated with serum total bilirubin and international normalized ratio. In addition, the serum SDF-l levels in survival were significantly lower compared with the non-survivals (P < 0.05). The area under the curve for the serum SDF-1 level in predicting 28-d mortality was 0.722 (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: This study provides the SDF-1 changes in patients with HBV-related ACLF. The SDF-1 Level at admission may serve as a promising prognostic marker for predicting short-term prognosis.
Keywords: Acute-on-chronic liver failure; CXC receptor 4; Hepatitis B; Prognosis; Stromal cell derived factor-1.
©The Author(s) 2024. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Soluble mannose receptor as a predictor of prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 7;25(37):5667-5675. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5667. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31602166 Free PMC article.
-
[Significance of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 prognostic evaluation in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 20;31(12):1306-1312. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20230214-00056. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38253075 Chinese.
-
Serum Clusterin: A Potential Marker for Assessing the Clinical Severity and Short-Term Prognosis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Dis Markers. 2020 Dec 12;2020:8814841. doi: 10.1155/2020/8814841. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 33381244 Free PMC article.
-
Low Serum Soluble Transferrin Receptor Levels Are Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Jun;201(6):2757-2764. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03385-2. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35969310
-
N-myc and STAT interactor correlates with severity and prognosis in acute-on-chronic liver failure of hepatitis B virus.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct;34(10):1800-1808. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14634. Epub 2019 Mar 7. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30771232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol. 2023;79:461–491. - PubMed
-
- Martin P, Nguyen MH, Dieterich DT, Lau DT, Janssen HLA, Peters MG, Jacobson IM. Treatment Algorithm for Managing Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in the United States: 2021 Update. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:1766–1775. - PubMed
-
- Lagarkova MA. Such Various Stem Cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2019;84:187–189. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

