Temporal and spatial variability of immunosuppressive therapies in transplant patients: An observational study in Italy
- PMID: 38994384
- PMCID: PMC11235261
- DOI: 10.3389/frtra.2022.1060621
Temporal and spatial variability of immunosuppressive therapies in transplant patients: An observational study in Italy
Abstract
Background: In immunosuppression after transplantation, several multi-drug approaches are used, involving calcineurin inhibitors (CNI: tacrolimus-TAC or cyclosporine-CsA), antimetabolites (antiMs), mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors (mTORis), and corticosteroids. However, data on immunosuppressive therapy by organ and its space-time variability are lacking.
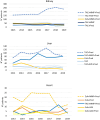
Methods: An Italian multicentre observational cohort study was conducted using health information systems. Patients with incident transplant during 2009-2019 and resident in four regions (Veneto, Lombardy, Lazio, and Sardinia) were enrolled. The post-transplant immunosuppressive regimen was evaluated by organ, region, and year.
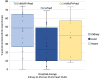
Results: The most dispensed regimen was triple-drug therapy for the kidneys [tacrolimus (TAC) + antiM + corticosteroids = 41.5%] and heart [cyclosporin + antiM + corticosteroids = 36.6%] and double-drug therapy for liver recipients (TAC + corticosteroids = 35.4%). Several differences between regions and years emerged with regard to agents and the number of drugs used.
Conclusion: A high heterogeneity in immunosuppressive therapy post-transplant was found. Further studies are needed in order to investigate the reasons for this variability and to evaluate the risk-benefit profile of treatment schemes adopted in clinical practice.
Keywords: drug utilization; immunosuppressive therapy; real-world evidence; solid organ transplant; space–time variability.
© 2023 Marino, Rosa, Finocchietti, Bellini, Poggi, Massari, Alegiani, Masiero, Ricci, Bedeschi, Puoti, Cardillo, Pierobon, Nordio, Ferroni, Zanforlini, Piccolo, Leoni, Ledda, Carta, Garau, Lucenteforte, Davoli, Addis and Belleudi.
Conflict of interest statement
MZ was employed by ARIA, S.p.a. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tsalouchos A, Salvadori M. La terapia immunosoppressiva nel trapianto di rene. Giornale Di Tecniche Nefrologiche e Dialitiche. (2019) 31(3):192–6. 10.1177/0394936219875392 - DOI
-
- BC Transplant. Clinical Guideline for transplant medication 2019 - AMB.03.007 Rev 11 Eff Date: 08-Jan-19.
-
- Enderby C, Keller CA. An overview of immunosuppression in solid organ transplantation. Am J Manag Care. (2015) 21(1 Suppl):S12–23. PMID: 25734416 - PubMed
-
- Heemann U, Abramowicz D, Spasovski G, Vanholder R. European renal best practice work group on kidney transplantation.endorsement of the KDIGO guidelines on kidney transplantation: a European renal best practice (ERBP) position statement. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2011) 26:2099–106. 10.1093/ndt/gfr169 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

