Postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts malignant cerebral edema following endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke
- PMID: 38994493
- PMCID: PMC11236612
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1394550
Postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts malignant cerebral edema following endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background and purpose: Malignant cerebral edema (MCE) is one of serious complications with high mortality following endovascular treatment (EVT) for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) with large vessel occlusion. We aimed to investigate the relationship between postoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and MCE after EVT.
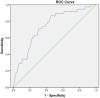
Methods: The clinical and imaging data of 175 patients with AIS of anterior circulation after EVT were studied. Admission and postoperative NLR were determined. The presence of MCE was evaluated on the computed tomography performed 24 h following EVT. The clinical outcomes were measured using the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) at 90-day after onset. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses were used to analyze the relationship between postoperative NLR and MCE. Optimal cutoff values of postoperative NLR to predict MCE were defined using receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Results: MCE was observed in 24% of the patients who underwent EVT and was associated with a lower rate of favorable clinical outcomes at 90-day. Multivariate logistic regression analysis demonstrated that baseline Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECT) score (OR = 0.614, 95% CI 0.502-0.750, p = 0.001), serum glucose (OR = 1.181, 95% CI 1.015-1.374, p = 0.031), and postoperative NLR (OR = 1.043, 95% CI 1.002-1.086, p = 0.041) were independently associated with MCE following EVT for AIS with large vessel occlusion. Postoperative NLR had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.743 for prediction MCE, and the optimal cutoff value was 6.15, with a sensitivity and specificity of 86.8% and 55%.
Conclusion: Elevated postoperative NLR is independently associated with malignant brain edema following EVT for AIS with large vessel occlusion, and may serve as an early predictive indicator for MCE after EVT.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; endovascular treatment; large vessel occlusion; malignant cerebral edema; neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Copyright © 2024 Zheng, Jiang, Guo and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Nomogram for Predicting Malignant Cerebral Edema After Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study.World Neurosurg. 2023 May;173:e548-e558. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.02.091. Epub 2023 Feb 25. World Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 36842531
-
Neutrophil Count Predicts Malignant Cerebellar Edema and Poor Outcome in Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion Receiving Endovascular Treatment: A Nationwide Registry-Based Study.Front Immunol. 2022 May 3;13:835915. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.835915. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35592334 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Endovascular Thrombectomy is Influenced by Systemic Inflammatory Index Through Malignant Brain Edema.Clin Interv Aging. 2022 Jul 2;17:1001-1012. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S365553. eCollection 2022. Clin Interv Aging. 2022. PMID: 35814350 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of futile recanalization after endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke.BMC Neurol. 2024 Jun 17;24(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03719-8. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38886670 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of Baseline Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients With Ischemic Stroke or Hemorrhagic Stroke: An Updated Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2019 Oct 4;10:1032. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01032. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31636598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arboix A, García-Eroles L, Oliveres M, Comes E, Sánchez MJ, Massons J. Malignant middle cerebral artery infarction: a clinical study of 32 patients. Rev Investig Clin. (2015) 67:64–70. PMID: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources