Diabetes Health Literacy, Drug Adherence and Factors Associated with Them among Urban Patients in Kerala, India
- PMID: 38994495
- PMCID: PMC7616181
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1632
Diabetes Health Literacy, Drug Adherence and Factors Associated with Them among Urban Patients in Kerala, India
Abstract
Aims: The study aimed to assess diabetes health literacy, adherence to diabetes medication, and its associated factors in Kerala, India, the most advanced Indian state in epidemiological transition with the highest literacy level in India.
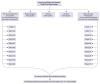
Materials and methods: We conducted a community-based cross-sectional study among 280 diabetes patients (mean age 62 years, male 42%) selected by multistage cluster sampling. Information on sociodemographic variables was collected using a pretested structured interview schedule. Diabetes health literacy was assessed using the revised Michigan Diabetes Knowledge test. Adherence to diabetes medication was assessed using the Hill-Bone subscale. Binary logistic regression analysis was done to find out the factors associated with diabetes health literacy and medication adherence.
Results: Good diabetes health literacy was reported by 35.7% [95% confidence interval (CI): 30.1-41.6] of the patients. Perfect adherence to diabetes medication was reported by 33.2% of patients (CI: 27.7-39.1). Patients who reported regular newspaper reading [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) 3.16; CI: 1.57-6.30], using the internet (AOR 2.23; CI: 1.11-4.50) and insulin use (AOR 2.60; CI: 1.35-5.00) were more likely to report good diabetes health literacy compared to their counterparts. Patients who reported reading health magazines (AOR 2.75; CI: 1.01-7.60) were more likely to report perfect medication adherence compared to those who did not.
Conclusion: Why diabetes health literacy and medication adherence were low among diabetes patients in the most literate state needs further investigation. Interventions to enhance diabetes health literacy and medication adherence may be undertaken among diabetes patients encouraging them to read newspapers and health magazines regularly and use the internet.
Keywords: Diabetes health literacy; Diabetes patients; India; Kerala; Medication adherence.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diabetic health literacy and its association with glycemic control among adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus attending the outpatient clinic of a university hospital in Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 8;15(4):e0231291. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231291. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32267893 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Medication Adherence and Associated Factors Among Patients With Diabetes Attending a Non-communicable Disease Clinic in a Community Health Centre in Eastern India.Cureus. 2023 Aug 20;15(8):e43779. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43779. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37731408 Free PMC article.
-
Health Literacy and Medication Adherence Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Jordan: A Cross-Sectional Study.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024 Sep 25;18:2019-2026. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S484135. eCollection 2024. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024. PMID: 39345761 Free PMC article.
-
Factors associated with medication adherence among people with diabetes mellitus in poor urban areas of Cambodia: A cross-sectional study.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 19;14(11):e0225000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225000. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31743349 Free PMC article.
-
Racial differences in medication adherence: A cross-sectional study of Medicare enrollees.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010 Apr;8(2):136-45. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2010.03.002. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010. PMID: 20439063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IDF diabetes atlas. 10th edition. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels: [accessed on 20 Dec 2022]. 2021. p. 37. [Internet]. [cited 2023 Feb 6]. Available from: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/
-
- Deepa M, Bhansali A, Anjana RM, et al. Knowledge and awareness of diabetes in urban and rural India: The Indian Council of Medical Research India Diabetes Study (Phase I): Indian Council of Medical Research India Diabetes 4. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2014;18(3):379–385. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.131191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources