Quantifying the vulnerabilities of the online public square to adversarial manipulation tactics
- PMID: 38994499
- PMCID: PMC11238850
- DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae258
Quantifying the vulnerabilities of the online public square to adversarial manipulation tactics
Abstract
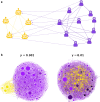
Social media, seen by some as the modern public square, is vulnerable to manipulation. By controlling inauthentic accounts impersonating humans, malicious actors can amplify disinformation within target communities. The consequences of such operations are difficult to evaluate due to the challenges posed by collecting data and carrying out ethical experiments that would influence online communities. Here we use a social media model that simulates information diffusion in an empirical network to quantify the impacts of adversarial manipulation tactics on the quality of content. We find that the presence of hub accounts, a hallmark of social media, exacerbates the vulnerabilities of online communities to manipulation. Among the explored tactics that bad actors can employ, infiltrating a community is the most likely to make low-quality content go viral. Such harm can be further compounded by inauthentic agents flooding the network with low-quality, yet appealing content, but is mitigated when bad actors focus on specific targets, such as influential or vulnerable individuals. These insights suggest countermeasures that platforms could employ to increase the resilience of social media users to manipulation.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of National Academy of Sciences.
Figures





References
-
- Ratkiewicz J, et al. 2011. Detecting and tracking political abuse in social media. Proceedings International AAAI Conference on Web and social media (ICWSM). 5(1):297–304.
-
- Metaxas PT, Mustafaraj E. 2012. Social media and the elections. Science. 338(6106):472–473. - PubMed
-
- Stewart LG, Arif A, Starbird K. 2018. Examining trolls and polarization with a retweet network. Proceedings ACM WSDM Workshop on Misinformation and Misbehavior Mining on the Web. 70(1):5–11.
-
- Arif A, Stewart LG, Starbird K. 2018. Acting the part: examining information operations within# BlackLivesMatter discourse. Proc ACM on Hum-Comput Interact. 2(CSCW):1–27.
-
- Lazer D, et al. 2018. The science of fake news. Science. 359(6380):1094–1096. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

