Data Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry Enhanced Personalized Glycosylation Profiling of Haptoglobin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 38994555
- PMCID: PMC11301664
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00227
Data Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry Enhanced Personalized Glycosylation Profiling of Haptoglobin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
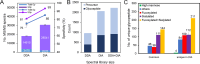
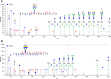
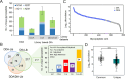
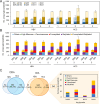
Aberrant glycosylation has gained significant interest for biomarker discovery. However, low detectability, complex glycan structures, and heterogeneity present challenges in glycoprotein assay development. Using haptoglobin (Hp) as a model, we developed an integrated platform combining functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and zwitterionic hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (ZIC-HILIC) for highly specific glycopeptide enrichment, followed by a data-independent acquisition (DIA) strategy to establish a deep cancer-specific Hp-glycosylation profile in hepatitis B virus (HBV, n = 5) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, n = 5) patients. The DIA strategy established one of the deepest Hp-glycosylation landscapes (1029 glycopeptides, 130 glycans) across serum samples, including 54 glycopeptides exclusively detected in HCC patients. Additionally, single-shot DIA searches against a DIA-based spectral library outperformed the DDA approach by 2-3-fold glycopeptide coverage across patients. Among the four N-glycan sites on Hp (N-184, N-207, N-211, N-241), the total glycan type distribution revealed significantly enhanced detection of combined fucosylated-sialylated glycans, which were the most dominant glycoforms identified in HCC patients. Quantitation analysis revealed 48 glycopeptides significantly enriched in HCC (p < 0.05), including a hybrid monosialylated triantennary glycopeptide on the N-184 site with nearly none-to-all elevation to differentiate HCC from the HBV group (HCC/HBV ratio: 2462 ± 766, p < 0.05). In summary, DIA-MS presents an unbiased and comprehensive alternative for targeted glycoproteomics to guide discovery and validation of glyco-biomarkers.
Keywords: data-independent acquisition (DIA); glycoprotein; haptoglobin; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu Y. C.; Yen H. Y.; Chen C. Y.; Chen C. H.; Cheng P. F.; Juan Y. H.; Chen C. H.; Khoo K. H.; Yu C. J.; Yang P. C.; Hsu T. L.; Wong C. H. Sialylation and fucosylation of epidermal growth factor receptor suppress its dimerization and activation in lung cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2011, 108 (28), 11332–11337. 10.1073/pnas.1107385108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

