Cholesterol Nanofiber Patches with Sustainable Oil Delivery Eliminate Inflammation in Atopic Skin
- PMID: 38994590
- PMCID: PMC11284794
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.4c09400
Cholesterol Nanofiber Patches with Sustainable Oil Delivery Eliminate Inflammation in Atopic Skin
Abstract
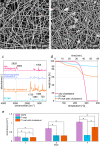
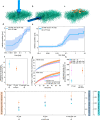
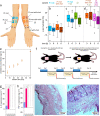
Atopic skin is dry and itchy and lacks integrity. Impaired skin barrier results from altered lipid composition of the skin. A crucial skin lipid, cholesterol, provides flexibility and homeostasis of the cell membranes' lipid bilayer. Cholesterol-based creams and natural oils, especially blackcurrant seed oil, are beneficial for skin care as they hydrate the skin and improve its integrity. The major atopic symptom, skin dryness, can be overcome by the application of porous patches enhanced with cholesterol and natural oil. The base of the patches is constructed of polyimide (PI) nanofibers with cholesterol coatings and externally added blackcurrant seed oil. The presence of cholesterol in PI mats hinders the passage of oil through the patches to the skin, resulting in sustained and prolonged skin hydration. The theoretical and numerical investigations of oil dynamics in porous mats confirmed the experimental results, showing a prolonged skin hydration effect up to 6 h. Additionally, as demonstrated by in vivo tests on atopic mice, cholesterol patches lower serum immunoglobulin E levels and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the skin, thereby accelerating skin healing. Our results hold great promise for the long-term application of the patches in atopic dermatitis treatment.
Keywords: atopic; cholesterol; oil delivery; oil transport; patches; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Moisturizing effect of skin patches with hydrophobic and hydrophilic electrospun fibers for atopic dermatitis.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021 Mar;199:111554. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111554. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021. PMID: 33421924
-
Adhesive Antibacterial Moisturizing Nanostructured Skin Patch for Sustainable Development of Atopic Dermatitis Treatment in Humans.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Jun 26;16(25):32128-32146. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c06662. Epub 2024 Jun 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38872576
-
Topical application of Artemisia annua L. essential oil ameliorates 2,4-dintrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Oct 28;333:118439. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118439. Epub 2024 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38862031
-
[Indications for sunflower oil concentrate in the treatment of atopic dermatitis].Rev Alerg Mex. 2006 Nov-Dec;53(6):217-25. Rev Alerg Mex. 2006. PMID: 17361756 Review. Spanish.
-
Electrospun fibers as carriers for topical drug delivery and release in skin bandages and patches for atopic dermatitis treatment.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023 Jan;15(1):e1829. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1829. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35817463 Review.
References
-
- Ring J.; Zink A.; Arents B. W. M.; Seitz I. A.; Mensing U.; Schielein M. C.; Wettemann N.; de Carlo G.; Fink-Wagner A. Atopic Eczema: Burden of Disease and Individual Suffering - Results from a Large EU Study in Adults. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33 (7), 1331–1340. 10.1111/jdv.15634. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

