Myeloid ectopic viral integration site 2 accelerates the progression of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38994634
- PMCID: PMC11464116
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14260
Myeloid ectopic viral integration site 2 accelerates the progression of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
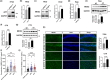
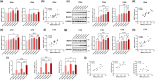
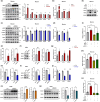
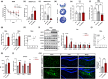
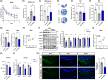
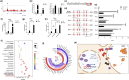
Amyloid plaques, a major pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD), are caused by an imbalance between the amyloidogenic and non-amyloidogenic pathways of amyloid precursor protein (APP). BACE1 cleavage of APP is the rate-limiting step for amyloid-β production and plaque formation in AD. Although the alteration of BACE1 expression in AD has been investigated, the underlying mechanisms remain unknown. In this study, we determined MEIS2 was notably elevated in AD models and AD patients. Alterations in the expression of MEIS2 can modulate the levels of BACE1. MEIS2 downregulation improved the learning and memory retention of AD mice and decreased the number of amyloid plaques. MEIS2 binds to the BACE1 promoter, positively regulates BACE1 expression, and accelerates APP amyloid degradation in vitro. Therefore, our findings suggest that MEIS2 might be a critical transcription factor in AD, since it regulates BACE1 expression and accelerates BACE1-mediated APP amyloidogenic cleavage. MEIS2 is a promising early intervention target for AD treatment.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; myeloid ectopic viral integration site 2; transcription pathway; β‐Site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1.
© 2024 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All other authors declare they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- (2021). 2021Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 17(3), 327–406. - PubMed
-
- Bahn, G. , Park, J. S. , Yun, U. J. , Lee, Y. J. , Choi, Y. , Park, J. S. , Baek, S. H. , Choi, B. Y. , Cho, Y. S. , Kim, H. K. , Han, J. , Sul, J. H. , Baik, S. H. , Lim, J. , Wakabayashi, N. , Bae, S. H. , Han, J. W. , Arumugam, T. V. , Mattson, M. P. , & Jo, D. G. (2019). NRF2/ARE pathway negatively regulates BACE1 expression and ameliorates cognitive deficits in mouse Alzheimer's models. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 116(25), 12516–12523. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bum‐Erdene, K. , Zhou, D. , Gonzalez‐Gutierrez, G. , Ghozayel, M. K. , Si, Y. , Xu, D. , Shannon, H. E. , Bailey, B. J. , Corson, T. W. , Pollok, K. E. , Wells, C. D. , & Meroueh, S. O. (2019). Small‐molecule covalent modification of conserved cysteine leads to allosteric inhibition of the TEAD·yap protein‐protein interaction. Cell Chemical Biology, 26(3), 378–389.e13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

