Luteolin enhances drug chemosensitivity by downregulating the FAK/PI3K/AKT pathway in paclitaxel‑resistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 38994756
- PMCID: PMC11265837
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5401
Luteolin enhances drug chemosensitivity by downregulating the FAK/PI3K/AKT pathway in paclitaxel‑resistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
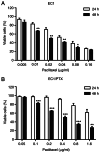
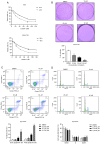
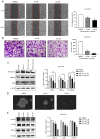
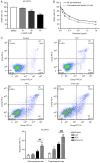
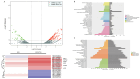
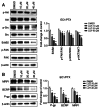
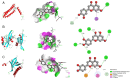
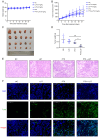
Drug resistance is a key factor underlying the failure of tumor chemotherapy. It enhances the stem‑like cell properties of cancer cells, tumor metastasis and relapse. Luteolin is a natural flavonoid with strong anti‑tumor effects. However, the mechanism(s) by which luteolin protects against paclitaxel (PTX)‑resistant cancer cell remains to be elucidated. The inhibitory effect of luteolin on the proliferation of EC1/PTX and EC1 cells was detected by cell counting kit‑8 assay. Colony formation and flow cytometry assays were used to assess clonogenic capacity, cell cycle and apoptosis. Wound healing and Transwell invasion tests were used to investigate the effects of luteolin on the migration and invasion of EC1/PTX cells. Western blotting was used to detect the protein levels of EMT‑related proteins and stem cell markers after sphere formation. Parental cells and drug‑resistant cells were screened by high‑throughput sequencing to detect the differential expression of RNA and differential genes. ELISA and western blotting were used to verify the screened PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, key proteins of which were explored by molecular docking. Hematoxylin and eosin staining and TUNEL staining were used to observe tumor xenografts on morphology and apoptosis in nude mice. The present study found that luteolin inhibited tumor resistance (inhibited proliferation, induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and hindered migration invasion, EMT and stem cell spherification) in vitro in PTX‑resistant esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. In addition, luteolin enhanced drug sensitivity and promoted the apoptosis of drug‑resistant ESCC cells in combination with PTX. Mechanistically, luteolin may inhibit the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by binding to the active sites of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Src and AKT. Notably, luteolin lowered the tumorigenic potential of PTX‑resistant ESCC cells but did not show significant toxicity in vivo. Luteolin enhanced drug chemosensitivity by downregulating the FAK/PI3K/AKT pathway in PTX‑resistant ESCC and could be a promising agent for the treatment of PTX‑resistant ESCC cancers.
Keywords: drug chemosensitivity; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; focal adhesion kinase/PI3K/AKT pathway; luteolin; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Luteolin attenuates cancer cell stemness in PTX-resistant oesophageal cancer cells through mediating SOX2 protein stability.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105939. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34655772
-
RIT1 suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis and predicts good prognosis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 22;9(11):1085. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0979-x. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30348939 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the regulatory mechanism of luteolin inhibiting WDR72 on the proliferation and metastasis of non small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 11;15(1):12398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96666-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40216870 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted anticancer potential of luteolin: involvement of NF-κB, AMPK/mTOR, PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Feb;33(2):505-525. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01596-8. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39543054 Review.
-
Aberrant DNA Methylation in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and its Clinical Implications in Systemic Chemotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 3;22(4):1002-1014. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109161. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39991775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of flavonoids in gastrointestinal cancer: Focus on signaling pathways and improvement strategies (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 Apr;31(4):109. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13474. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40017144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer through epigenetic modulations by dietary flavonoid Galangin and its combination with SAHA.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Apr 2;23(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02174-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40176095 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating network pharmacology and molecular modeling to decipher the anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma mechanisms of Bidens pilosa L.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 21;16(1):1589. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03441-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40836204 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
