Research progress on long non‑coding RNAs in non‑infectious spinal diseases (Review)
- PMID: 38994759
- PMCID: PMC11267249
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13288
Research progress on long non‑coding RNAs in non‑infectious spinal diseases (Review)
Abstract
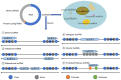
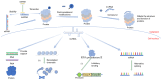
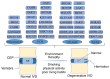
Spinal diseases, including intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD), ankylosing spondylitis, spinal cord injury and other non‑infectious spinal diseases, severely affect the quality of life of patients. Current treatments for IDD and other spinal diseases can only relieve symptoms and do not completely cure the disease. Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore the causes of these diseases and develop new treatment approaches. Long non‑coding RNA (lncRNA), a form of non‑coding RNA, is abundant in diverse sources, has numerous functions, and plays an important role in the occurrence and development of spinal diseases such as IDD. However, the mechanism of action of lncRNAs has not been fully elucidated, and significant challenges remain in the use of lncRNAs as new therapeutic targets. The present article reviews the sources, classification and functions of lncRNAs, and introduces the role of lncRNAs in spinal diseases, such as IDD, and their therapeutic potential.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; intervertebral disc degeneration; long non‑coding RNAs; non‑coding RNAs; spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differentially-expressed mRNAs, microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration identified by RNA-sequencing.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):1026-1039. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1899533. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 33764282 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Long Noncoding RNAs in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by RNA Sequencing.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3684875. doi: 10.1155/2016/3684875. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28097131 Free PMC article.
-
The potential mechanisms and application prospects of non-coding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 8;13:1081185. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1081185. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36568075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and functions of long noncoding RNAs in intervertebral disc degeneration.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Jul;235:153959. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153959. Epub 2022 May 28. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35653923 Review.
-
Emerging evidence on noncoding-RNA regulatory machinery in intervertebral disc degeneration: a narrative review.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Nov 16;22(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02353-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33198793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of LncRNA PSMA3-AS1 in prostate cancer and its potential regulatory mechanism.Hereditas. 2025 Jul 12;162(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00485-6. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40652273 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effect and experimental research progress of pleotropic statins in intervertebral disc degeneration.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jan 31;20(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05487-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 39891158 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wong CK, Mak RY, Kwok TS, Tsang JS, Leung MY, Funabashi M, Macedo LG, Dennett L, Wong AY. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with non-specific chronic low back pain in community-dwelling older adults aged 60 years and older: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pain. 2022;23:509–534. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2021.07.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2017, corp-author. Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators: Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

