Cx40 Levels Regulate Hypoxia-Induced Changes in the Migration, Proliferation, and Formation of Gap Junction Plaques in an Extravillous Trophoblast Cell Model
- PMID: 38995001
- PMCID: PMC11240472
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13131150
Cx40 Levels Regulate Hypoxia-Induced Changes in the Migration, Proliferation, and Formation of Gap Junction Plaques in an Extravillous Trophoblast Cell Model
Abstract
Background: Extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs) form stratified columns at the placenta-uterus interface. In the closest part to fetal structures, EVTs have a proliferative phenotype, whereas in the closest part to maternal structures, they present a migratory phenotype. During the placentation process, Connexin 40 (Cx40) participates in both the proliferation and migration of EVTs, which occurs under hypoxia. However, a possible interaction between hypoxia and Cx40 has not yet been established.
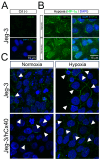
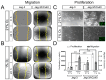
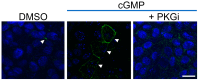
Methods: We developed two cellular models, one with "low Cx40" (Jeg-3), which reflected the expression of this protein found in migratory EVTs, and one with "high Cx40" (Jeg-3/hCx40), which reflected the expression of this protein in proliferative cells. We analyzed the migration and proliferation of these cells under normoxic and hypoxic conditions for 24 h. Jeg-3 cells under hypoxia increased their migratory capacity over their proliferative capacity. However, in Jeg-3/hCx40, the opposite effect was induced. On the other hand, hypoxia promoted gap junction (GJ) plaque formation between neighboring Jeg-3 cells. Similarly, the activation of a nitro oxide (NO)/cGMP/PKG-dependent pathway induced an increase in GJ-plaque formation in Jeg-3 cells.
Conclusions: The expression patterns of Cx40 play a crucial role in shaping the responses of EVTs to hypoxia, thereby influencing their migratory or proliferative phenotype. Simultaneously, hypoxia triggers an increase in Cx40 gap junction (GJ) plaque formation through a pathway dependent on NO.
Keywords: connexins; extravillous trophoblast; gap junction channels; nitric oxide; placenta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Connexin expression and gap junctional intercellular communication in human first trimester trophoblast.Mol Hum Reprod. 2002 Nov;8(11):1005-13. doi: 10.1093/molehr/8.11.1005. Mol Hum Reprod. 2002. PMID: 12397213
-
Connexin expression patterns in human trophoblast cells during placental development.Placenta. 1999 Nov;20(8):627-38. doi: 10.1053/plac.1999.0434. Placenta. 1999. PMID: 10527817
-
Functional formation of heterotypic gap junction channels by connexins-40 and -43.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(5):433-43. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.949188. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25483586 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of gap junctional communication and connexin expression in trophoblast differentiation of the human placenta.Histol Histopathol. 2001 Jan;16(1):285-95. doi: 10.14670/HH-16.285. Histol Histopathol. 2001. PMID: 11193204 Review.
-
Cardiac Cx43, Cx40 and Cx45 co-assembling: involvement of connexins epitopes in formation of hemichannels and Gap junction channels.BMC Cell Biol. 2017 Jan 17;18(Suppl 1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12860-016-0118-4. BMC Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28124623 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can the Tumor Microenvironment Alter Ion Channels? Unraveling Their Role in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 6;17(7):1244. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071244. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short communication: Upregulation of hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced Shc3 by downregulated miR-455-5p, suppresses trophoblast invasion and is associated with placental inflammation and angiogenesis in preeclampsia.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 10;20(1):e0314544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0314544. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39792965 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

