Natural Products for Preventing and Managing Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 38995002
- PMCID: PMC11240786
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13131151
Natural Products for Preventing and Managing Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline anticancer agent that is highly effective in the treatment of solid tumors. Given the multiplicity of mechanisms involved in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, it is difficult to identify a precise molecular target for toxicity. The findings of a literature review suggest that natural products may offer cardioprotective benefits against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, both in vitro and in vivo. However, further confirmatory studies are required to substantiate this claim. It is of the utmost importance to direct greater attention towards the intricate signaling networks that are of paramount importance for the survival and dysfunction of cardiomyocytes. Notwithstanding encouraging progress made in preclinical studies of natural products for the prevention of DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, these have not yet been translated for clinical use. One of the most significant obstacles hindering the development of cardioprotective adjuvants based on natural products is the lack of adequate bioavailability in humans. This review presents an overview of current knowledge on doxorubicin DOX-induced cardiotoxicity, with a focus on the potential benefits of natural compounds and herbal preparations in preventing this adverse effect. As literature search engines, the browsers in the Scopus, PubMed, Web of Science databases and the ClinicalTrials.gov register were used.
Keywords: cardio prevention; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; plant compounds; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

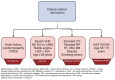
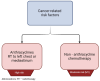

References
-
- Osoro I., Sharma A., Amir M., Vohra M., Kumar R., Kumar H., Zargar A., Bangar H. Prevention and Management of Anthracycline Induced Cardiotoxicity: A Review. Health Sci. Rev. 2022;5:100070. doi: 10.1016/j.hsr.2022.100070. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

