Cefiderocol heteroresistance associated with mutations in TonB-dependent receptor genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of clinical origin
- PMID: 38995033
- PMCID: PMC11304687
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00127-24
Cefiderocol heteroresistance associated with mutations in TonB-dependent receptor genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of clinical origin
Abstract
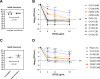
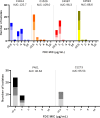
The siderophore-cephalosporin cefiderocol (FDC) presents a promising treatment option for carbapenem-resistant (CR) P. aeruginosa (PA). FDC circumvents traditional porin and efflux-mediated resistance by utilizing TonB-dependent receptors (TBDRs) to access the periplasmic space. Emerging FDC resistance has been associated with loss of function mutations within TBDR genes or the regulatory genes controlling TBDR expression. Further, difficulties with antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) and unexpected negative clinical treatment outcomes have prompted concerns for heteroresistance, where a single lineage isolate contains resistant subpopulations not detectable by standard AST. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of TBDR mutations among clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa and the phenotypic effect on FDC susceptibility and heteroresistance. We evaluated the sequence of pirR, pirS, pirA, piuA, or piuD from 498 unique isolates collected before the introduction of FDC from four clinical sites in Portland, OR (1), Houston, TX (2), and Santiago, Chile (1). At some clinical sites, TBDR mutations were seen in up to 25% of isolates, and insertion, deletion, or frameshift mutations were predicted to impair protein function were seen in 3% of all isolates (n = 15). Using population analysis profile testing, we found that P. aeruginosa with major TBDR mutations were enriched for a heteroresistant phenotype and undergo a shift in the susceptibility distribution of the population as compared to susceptible strains with wild-type TBDR genes. Our results indicate that mutations in TBDR genes predate the clinical introduction of FDC, and these mutations may predispose to the emergence of FDC resistance.
Keywords: Gram-negative resistance; Pseudomonas aeurginosa; TonB-dependent receptor; beta-lactamases; cefiderocol; heteroresistance; multi-drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
W.R.M. has received grant support from Merck and royalties from UpToDate. C.A.A. has received royalties from UpToDate. All other authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures


Update of
-
Cefiderocol heteroresistance associated with mutations in TonB-dependent receptor genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of clinical origin.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 31:2024.01.30.578008. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.30.578008. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Aug 7;68(8):e0012724. doi: 10.1128/aac.00127-24. PMID: 38352536 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- CDC . 2019. Antimicrobial resistance threats in the United States. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Atlanta, GA.
-
- Tacconelli E, Carrara E, Savoldi A, Harbarth S, Mendelson M, Monnet DL, Pulcini C, Kahlmeter G, Kluytmans J, Carmeli Y, Ouellette M, Outterson K, Patel J, Cavaleri M, Cox EM, Houchens CR, Grayson ML, Hansen P, Singh N, Theuretzbacher U, Magrini N, WHO Pathogens Priority List Working Group . 2018. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis 18:318–327. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30753-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satlin MJ, Simner PJ, Slover CM, Yamano Y, Nagata TD, Portsmouth S. 2023. Cefiderocol treatment for patients with multidrug- and carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in the compassionate use program. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 67:e0019423. doi: 10.1128/aac.00194-23 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M, Echols R, Matsunaga Y, Ariyasu M, Doi Y, Ferrer R, Lodise TP, Naas T, Niki Y, Paterson DL, Portsmouth S, Torre-Cisneros J, Toyoizumi K, Wunderink RG, Nagata TD. 2021. Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis 21:226–240. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30796-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI152999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI141349/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI134637/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- AI141349/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- T32 AI055449/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI121296/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI148342/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- AI175821/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AI148342/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI121296/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R01 AI134637/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI152999/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- R21 AI175821/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

