Mendelian randomization analysis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with risks of ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 38995229
- PMCID: PMC11242227
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13795
Mendelian randomization analysis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with risks of ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Objective: This study is designed to explore the potential causal relationship between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) while investigating the genetic basis shared by these inflammatory diseases.
Methods: Significant single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with UC, psoriasis, and PsA were selected as genetic instrumental variables using Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) datasets. Additionally, Mendelian randomization (MR) methods, including inverse-variance weighting (IVW), MR-Egger regression, and Weighted Median (WME), were utilized to evaluate the causal relationships between these diseases. Moreover, sensitivity analysis and heterogeneity testing were conducted to validate the stability of the results.
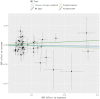
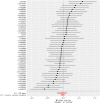
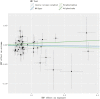
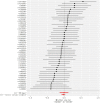
Results: A total of 123 significant SNPs associated with psoriasis, PsA, and UC were identified as genetic instrumental variables based on GWAS datasets. The analysis revealed a 36% increased risk of UC with psoriasis (odds ratio [OR] = 1.350, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.065-1.729, P = 0.012) and a 32.9% increased risk of UC with PsA (OR = 1.329, 95% CI = 1.176-1.592, P < 0.001). Further analysis showed a 43.5% increased risk of psoriasis with UC (OR = 1.435, 95% CI = 1.274-1.831, P < 0.001) and a 45.8% increased risk of PsA with UC (OR = 1.458, 95% CI = 1.166-1.822, P = 0.0013). In addition, sensitivity analysis and heterogeneity testing demonstrated the high stability of these results. Particularly, neither MR-Egger regression analysis nor leave-one-out analysis revealed significant heterogeneity or pleiotropy bias, indicating the reliability of these causal estimates. Moreover, the use of the MR-PRESSO further confirmed the positive correlation between psoriasis and UC, and the corrected estimates remained consistent with IVW analysis results after excluding potential outlier SNPs, enhancing the credibility of the analysis.
Conclusions: This study strengthens the understanding of the genetic and causal relationships among UC, psoriasis, and PsA through GWAS and MR methods, revealing the genetic basis they may share. These findings not only provide a novel perspective on the comorbidity mechanisms of these diseases but also offer a valuable reference for the development of future treatment strategies and intervention measures.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization analysis; psoriasis; psoriatic arthritis.
© 2024 The Author(s). Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global and regional genetic association analysis of ulcerative colitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus and causal validation analysis of two-sample two-way Mendelian randomization.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 22;15:1375915. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1375915. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39650653 Free PMC article.
-
Causal associations between both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and multiple autoimmune diseases: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 25;15:1422626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1422626. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39119335 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Mendelian Randomization Studies in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review.J Invest Dermatol. 2023 May;143(5):762-776.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.11.014. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Invest Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36822971
-
Vasectomy and prostate cancer risk: a pooled of cohort studies and Mendelian randomization analysis.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 24;25(1):332. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13750-8. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39994603 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a genome-wide Mendelian randomization study.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Apr;44(4):1607-1616. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07374-3. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39985656
-
Association of partial infections with the risk of psoriasis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Skin Res Technol. 2024 Aug;30(8):e70002. doi: 10.1111/srt.70002. Skin Res Technol. 2024. Retraction in: Skin Res Technol. 2025 Jun;31(6):e70196. doi: 10.1111/srt.70196. PMID: 39167023 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Jin JQ, Elhage KG, Spencer RK, et al. Mendelian randomization studies in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review. J Invest Dermatol. 2023;143(5):762‐776.e3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

