A curated rotamer library for common post-translational modifications of proteins
- PMID: 38995731
- PMCID: PMC11254353
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae444
A curated rotamer library for common post-translational modifications of proteins
Abstract
Motivation: Sidechain rotamer libraries of the common amino acids of a protein are useful for folded protein structure determination and for generating ensembles of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). However, much of protein function is modulated beyond the translated sequence through the introduction of post-translational modifications (PTMs).
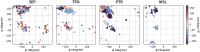
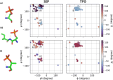
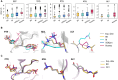
Results: In this work, we have provided a curated set of side chain rotamers for the most common PTMs derived from the RCSB PDB database, including phosphorylated, methylated, and acetylated sidechains. Our rotamer libraries improve upon existing methods such as SIDEpro, Rosetta, and AlphaFold3 in predicting the experimental structures for PTMs in folded proteins. In addition, we showcase our PTM libraries in full use by generating ensembles with the Monte Carlo Side Chain Entropy (MCSCE) for folded proteins, and combining MCSCE with the Local Disordered Region Sampling algorithms within IDPConformerGenerator for proteins with intrinsically disordered regions.
Availability and implementation: The codes for dihedral angle computations and library creation are available at https://github.com/THGLab/ptm_sc.git.
Published by Oxford University Press 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Update of
-
A Curated Rotamer Library for Common Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:arXiv:2405.03120v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2024 Jul 1;40(7):btae444. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae444. PMID: 38764597 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A Curated Rotamer Library for Common Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 6:arXiv:2405.03120v1. ArXiv. 2024. Update in: Bioinformatics. 2024 Jul 1;40(7):btae444. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae444. PMID: 38764597 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
IDPConformerGenerator: A Flexible Software Suite for Sampling the Conformational Space of Disordered Protein States.J Phys Chem A. 2022 Sep 8;126(35):5985-6003. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.2c03726. Epub 2022 Aug 28. J Phys Chem A. 2022. PMID: 36030416 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Function by Post-translational Modifications.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):6696-705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.695056. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26851279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating post-translational modifications and unnatural amino acids into high-throughput modeling of protein structures.Bioinformatics. 2014 Jun 15;30(12):1681-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu106. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24574112 Free PMC article.
-
Dancing Protein Clouds: The Strange Biology and Chaotic Physics of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):6681-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.685859. Epub 2016 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26851286 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amino-Acid Characteristics in Protein Native State Structures.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 7;14(7):805. doi: 10.3390/biom14070805. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062519 Free PMC article.
-
FakeRotLib: expedient non-canonical amino acid parameterization in Rosetta.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 2:2025.02.27.640629. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.27.640629. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40093079 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Computational Methods to Investigate Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and their Complexes.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 3:arXiv:2409.02240v1. ArXiv. 2024. PMID: 39279844 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
AlphaFold 3: an unprecedent opportunity for fundamental research and drug development.Precis Clin Med. 2025 Jul 1;8(3):pbaf015. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbaf015. eCollection 2025 Sep. Precis Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40799364 Free PMC article. Review.

