Early Astrocytic Dysfunction Is Associated with Mistuned Synapses as well as Anxiety and Depressive-Like Behavior in the AppNL-F Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38995780
- PMCID: PMC11307019
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-231461
Early Astrocytic Dysfunction Is Associated with Mistuned Synapses as well as Anxiety and Depressive-Like Behavior in the AppNL-F Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Unfortunately, efficient and affordable treatments are still lacking for this neurodegenerative disorder, it is therefore urgent to identify new pharmacological targets. Astrocytes are playing a crucial role in the tuning of synaptic transmission and several studies have pointed out severe astrocyte reactivity in AD. Reactive astrocytes show altered physiology and function, suggesting they could have a role in the early pathophysiology of AD.
Objective: We aimed to characterize early synaptic impairments in the AppNL-F knock-in mouse model of AD, especially to understand the contribution of astrocytes to early brain dysfunctions.
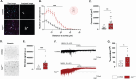
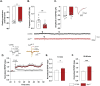
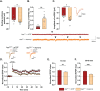
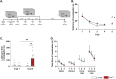
Methods: The AppNL-F mouse model carries two disease-causing mutations inserted in the amyloid precursor protein gene. This strain does not start to develop amyloid-β plaques until 9 months of age. Thanks to electrophysiology, we investigated synaptic function, at both neuronal and astrocytic levels, in 6-month-old animals and correlate the synaptic activity with emotional behavior.
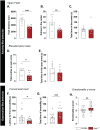
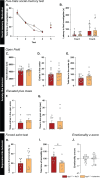
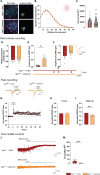
Results: Electrophysiological recordings in the hippocampus revealed an overall synaptic mistuning at a pre-plaque stage of the pathology, associated to an intact social memory but a stronger depressive-like behavior. Astrocytes displayed a reactive-like morphology and a higher tonic GABA current compared to control mice. Interestingly, we here show that the synaptic impairments in hippocampal slices are partially corrected by a pre-treatment with the monoamine oxidase B blocker deprenyl or the fast-acting antidepressant ketamine (5 mg/kg).
Conclusions: We propose that reactive astrocytes can induce synaptic mistuning early in AD, before plaques deposition, and that these changes are associated with emotional symptoms.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; App knock-in mice; LTP; MAO-B; depression; synapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Ferri CP, Sousa R, Albanese E, Ribeiro WS, MHonyashiki M, Acosta D, Blom M, Dudgeon S, Frantz N, Geiger A, Jensen A, Ketteringham A, Kinnaird L, Martensson B, Rees G, Schaper F, Splaine M, Tami T, Westerlind K, Wortmann M (2009) World Alzheimer’s Report 2009. Alzheimer’s Disease International, London.
-
- Shen LX, Yang YX, Kuo K, Li HQ, Chen SD, Chen KL, Dong Q, Tan L, Yu JT (2021) Social isolation, social interaction, and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. J Alzheimers Dis 80, 665–672. - PubMed
-
- Zubenko GS, Zubenko WN, McPherson S, Spoor E, Marin DB, Farlow MR, Smith GE, Geda YE, Cummings JL, Petersen RC, Sunderland T (2003) A collaborative study of the emergence and clinical features of the major depressive syndrome of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Psychiatry 160, 857–866. - PubMed
-
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, Bateman RJ, Chen C, Gee M, Kanekiyo M, Li D, Reyderman L, Cohen S, Froelich L, Katayama S, Sabbagh M, Vellas B, Watson D, Dhadda S, Irizarry M, Kramer LD, Iwatsubo T (2023) Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 388, 9–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

