Octopamine is required for successful reproduction in the classical insect model, Rhodnius prolixus
- PMID: 38995904
- PMCID: PMC11244822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306611
Octopamine is required for successful reproduction in the classical insect model, Rhodnius prolixus
Abstract
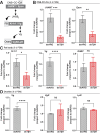
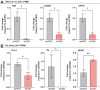
In insects, biogenic amines function as neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, and neurohormones, influencing various behaviors, including those related to reproduction such as response to sex pheromones, oogenesis, oviposition, courtship, and mating. Octopamine (OA), an analog of the vertebrate norepinephrine, is synthesized from the biogenic amine tyramine by the enzyme tyramine β-hydroxylase (TβH). Here, we investigate the mechanisms and target genes underlying the role of OA in successful reproduction in females of Rhodnius prolixus, a vector of Chagas disease, by downregulating TβH mRNA expression (thereby reducing OA content) using RNA interference (RNAi), and in vivo and ex vivo application of OA. Injection of females with dsTβH impairs successful reproduction at least in part, by decreasing the transcript expression of enzymes involved in juvenile hormone biosynthesis, the primary hormone for oogenesis in R. prolixus, thereby interfering with oogenesis, ovulation and oviposition. This study offers valuable insights into the involvement of OA for successful reproduction in R. prolixus females. Understanding the reproductive biology of R. prolixus is crucial in a medical context for controlling the spread of the disease.
Copyright: © 2024 Leyria et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
How Tyramine β-Hydroxylase Controls the Production of Octopamine, Modulating the Mobility of Beetles.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 14;19(3):846. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030846. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29538302 Free PMC article.
-
Bicaudal C is required for the function of the follicular epithelium during oogenesis in Rhodnius prolixus.Dev Genes Evol. 2021 Mar;231(1-2):33-45. doi: 10.1007/s00427-021-00673-0. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Dev Genes Evol. 2021. PMID: 33704576
-
Functional characterization of vitellogenin unveils novel roles in RHBP uptake and lifespan regulation in the insect vector Rhodnius prolixus.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2025 May;180:104301. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2025.104301. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40089120
-
The interaction of feeding and mating in the hormonal control of egg production in Rhodnius prolixus.J Insect Physiol. 2007 Mar;53(3):208-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2006.10.002. Epub 2006 Oct 12. J Insect Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17126364 Review.
-
The hormonal and neural control of egg production in the historically important model insect, Rhodnius prolixus: A review, with new insights in this post-genomic era.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2022 Jun 1;321-322:114030. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2022.114030. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35317995 Review.
References
-
- Orchard I. Octopamine in insects: neurotransmitter, neurohormone, and neuromodulator. Can J Zool. 1992;60: 659–669.
-
- Lange AB, Orchard I. Biogenic monoamines in the control of triatomine physiology with emphasis on Rhodnius prolixus. In: Guarneri A, Lorenzo M, editors. Triatominae—The biology of Chagas disease vectors. 1st ed. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland AG; 2021. p. 145–66.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

