Initiator cell death event induced by SARS-CoV-2 in the human airway epithelium
- PMID: 38996010
- PMCID: PMC11970318
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adn0178
Initiator cell death event induced by SARS-CoV-2 in the human airway epithelium
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Research Article "Initiator cell death event induced by SARS-CoV-2 in the human airway epithelium" by K. Liang et al.Sci Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;9(100):eadt4547. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adt4547. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Sci Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39423286 No abstract available.
Abstract
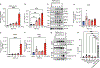
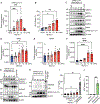
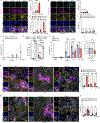
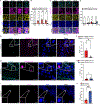
Virus-induced cell death is a key contributor to COVID-19 pathology. Cell death induced by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is well studied in myeloid cells but less in its primary host cell type, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-expressing human airway epithelia (HAE). SARS-CoV-2 induces apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in HAE organotypic cultures. Single-cell and limiting-dilution analysis revealed that necroptosis is the primary cell death event in infected cells, whereas uninfected bystanders undergo apoptosis, and pyroptosis occurs later during infection. Mechanistically, necroptosis is induced by viral Z-RNA binding to Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1) in HAE and lung tissues from patients with COVID-19. The Delta (B.1.617.2) variant, which causes more severe disease than Omicron (B1.1.529) in humans, is associated with orders of magnitude-greater Z-RNA/ZBP1 interactions, necroptosis, and disease severity in animal models. Thus, Delta induces robust ZBP1-mediated necroptosis and more disease severity.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.-Y.T is a cofounder of IMMvention Therapeutix.
Figures


References
-
- Wang Y, Perlman S, COVID-19: Inflammatory Profile. Annu Rev Med 73, 65–80 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R21 AI163822/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G20 AI167200/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007151/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI158314/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES032643/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI029564/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI029564/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE033330/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK130381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE026728/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE029255/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- UC6 AI058607/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI029564/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL166508/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI175479/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI158314/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA232109/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI141333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK065988/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

