Three-dimensional genome architecture persists in a 52,000-year-old woolly mammoth skin sample
- PMID: 38996487
- PMCID: PMC12128189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.002
Three-dimensional genome architecture persists in a 52,000-year-old woolly mammoth skin sample
Abstract
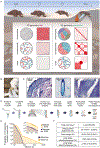
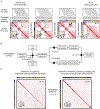
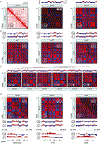
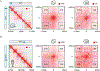
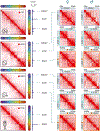
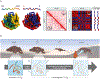
Analyses of ancient DNA typically involve sequencing the surviving short oligonucleotides and aligning to genome assemblies from related, modern species. Here, we report that skin from a female woolly mammoth (†Mammuthus primigenius) that died 52,000 years ago retained its ancient genome architecture. We use PaleoHi-C to map chromatin contacts and assemble its genome, yielding 28 chromosome-length scaffolds. Chromosome territories, compartments, loops, Barr bodies, and inactive X chromosome (Xi) superdomains persist. The active and inactive genome compartments in mammoth skin more closely resemble Asian elephant skin than other elephant tissues. Our analyses uncover new biology. Differences in compartmentalization reveal genes whose transcription was potentially altered in mammoths vs. elephants. Mammoth Xi has a tetradic architecture, not bipartite like human and mouse. We hypothesize that, shortly after this mammoth's death, the sample spontaneously freeze-dried in the Siberian cold, leading to a glass transition that preserved subfossils of ancient chromosomes at nanometer scale.
Keywords: Hi-C; X inactivation; ancient DNA; chromatin loops; fossil; genome architecture; genome assembly; glass transition; vitrification; woolly mammoth.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests E.L.A., M.T.P.G., and L.D. are on the scientific advisory board of Colossal Biosciences and hold stock options. From 2021 to 2023, M.A.M.-R. received consulting honoraria from Acuity Spatial Genomics. E.L.A. and O.D. are inventors on US provisional patent applications 16/308,386 (E.L.A. and O.D., filed 12/7/2018), 16/247,502 (E.L.A. and O.D., 1/14/2019), and PCT/US2020/064704 (E.L.A., 12/11/2020) by the Baylor College of Medicine and the Broad Institute, relating to the assembly methods in this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Higuchi R, Bowman B, Freiberger M, Ryder OA, and Wilson AC (1984). Dna-Sequences From the Quagga, an Extinct Member of the Horse Family. Nature 312, 282–284. - PubMed
-
- Pääbo S. (1985). Molecular cloning of Ancient Egyptian mummy DNA. Nature 314, 644–645. - PubMed
-
- Miller W, Drautz DI, Ratan A, Pusey B, Qi J, Lesk AM, Tomsho LP, Packard MD, Zhao F, Sher A, et al. (2008). Sequencing the nuclear genome of the extinct woolly mammoth. Nature 456, 387–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

