Rational design of lipid nanoparticles: overcoming physiological barriers for selective intracellular mRNA delivery
- PMID: 38996568
- PMCID: PMC11323194
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102499
Rational design of lipid nanoparticles: overcoming physiological barriers for selective intracellular mRNA delivery
Abstract
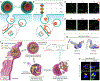
This review introduces the typical delivery process of messenger RNA (mRNA) nanomedicines and concludes that the delivery involves a at least four-step SCER cascade and that high efficiency at every step is critical to guarantee high overall therapeutic outcomes. This SCER cascade process includes selective organ-targeting delivery, cellular uptake, endosomal escape, and cytosolic mRNA release. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have emerged as a state-of-the-art vehicle for in vivo mRNA delivery. The review emphasizes the importance of LNPs in achieving selective, efficient, and safe mRNA delivery. The discussion then extends to the technical and clinical considerations of LNPs, detailing the roles of individual components in the SCER cascade process, especially ionizable lipids and helper phospholipids. The review aims to provide an updated overview of LNP-based mRNA delivery, outlining recent innovations and addressing challenges while exploring future developments for clinical translation over the next decade.
Keywords: Cellular uptake; Cytosolic mRNA release; Endosomal escape; Lipid nanoparticle; Targeted mRNA delivery.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
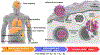


References
-
- Tavernier G; Andries O; Demeester J; Sanders NN; De Smedt SC; Rejman J, mRNA as gene therapeutic: how to control protein expression. J Control Release 2011, 150 (3), 238–47. - PubMed
-
- Tahmasebi S; Alain T; Rajasekhar VK; Zhang J-P; Prager-Khoutorsky M; Khoutorsky A; Dogan Y; Gkogkas CG; Petroulakis E; Sylvestre A, Multifaceted regulation of somatic cell reprogramming by mRNA translational control. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14 (5), 606–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

