Adeno-associated virus delivered CXCL9 sensitizes glioblastoma to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade
- PMID: 38997283
- PMCID: PMC11245621
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49989-1
Adeno-associated virus delivered CXCL9 sensitizes glioblastoma to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade
Abstract
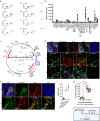
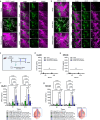
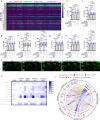
There are numerous mechanisms by which glioblastoma cells evade immunological detection, underscoring the need for strategic combinatorial treatments to achieve appreciable therapeutic effects. However, developing combination therapies is difficult due to dose-limiting toxicities, blood-brain-barrier, and suppressive tumor microenvironment. Glioblastoma is notoriously devoid of lymphocytes driven in part by a paucity of lymphocyte trafficking factors necessary to prompt their recruitment and activation. Herein, we develop a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy that enables focal and stable reconstitution of the tumor microenvironment with C-X-C motif ligand 9 (CXCL9), a powerful call-and-receive chemokine for lymphocytes. By manipulating local chemokine directional guidance, AAV-CXCL9 increases tumor infiltration by cytotoxic lymphocytes, sensitizing glioblastoma to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade in female preclinical tumor models. These effects are accompanied by immunologic signatures evocative of an inflamed tumor microenvironment. These findings support AAV gene therapy as an adjuvant for reconditioning glioblastoma immunogenicity given its safety profile, tropism, modularity, and off-the-shelf capability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


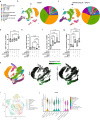


Update of
-
CXCL9 recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) virotherapy sensitizes glioblastoma (GBM) to anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 14:rs.3.rs-3463730. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3463730/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 12;15(1):5871. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49989-1. PMID: 38014191 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Melero I, Rouzaut A, Motz GT, Coukos G. T-cell and NK-cell infiltration into solid tumors: a key limiting factor for efficacious cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:522–526. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

