Development of implantable electrode based on bioresorbable Mg alloy for tissue welding application
- PMID: 38997318
- PMCID: PMC11245471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67077-8
Development of implantable electrode based on bioresorbable Mg alloy for tissue welding application
Abstract
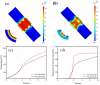
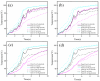
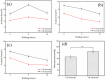
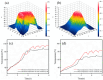
An implantable electrode based on bioresorbable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy was developed for next-generation radiofrequency (RF) tissue welding application, aiming to reduce thermal damage and enhance anastomotic strength. The Mg alloy electrode was designed with different structural features of cylindrical surface (CS) and continuous long ring (LR) in the welding area, and the electrothermal simulations were studied by finite element analysis (FEA). Meanwhile, the temperature variation during tissue welding was monitored and the anastomotic strength of welded tissue was assessed by measuring the avulsion force and burst pressure. FEA results showed that the mean temperature in the welding area and the proportion of necrotic tissue were significantly reduced when applying an alternating current of 110 V for 10 s to the LR electrode. In the experiment of tissue welding ex vivo, the maximum and mean temperatures of tissues welded by the LR electrode were also significantly reduced and the anastomotic strength of welded tissue could be obviously improved. Overall, an ideal welding temperature and anastomotic strength which meet the clinical requirement can be obtained after applying the LR electrode, suggesting that Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy with optimal structure design shows great potential to develop implantable electrode for next-generation RF tissue welding application.
Keywords: Anastomotic strength; Electrothermal simulation; Implantable electrode; Mg alloy; Radiofrequency tissue welding; Structural design.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel electrode for reducing tissue thermal damage in radiofrequency-induced intestinal anastomosis.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2024 Apr;33(2):80-89. doi: 10.1080/13645706.2023.2297774. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2024. PMID: 38147884
-
Optimizing mechanical properties of laser-welded gold alloy through heat treatment.Dent Mater. 2004 Sep;20(7):630-4. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2003.08.004. Dent Mater. 2004. PMID: 15236937
-
Reduced Thermal Damage Achieved by High-Conductivity Hydrogel in RF Energy Tissue Welding.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 Mar 10;11(3):1391-1401. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.4c02292. Epub 2025 Feb 22. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 39985434
-
Welding of High Entropy Alloys-A Review.Entropy (Basel). 2019 Apr 24;21(4):431. doi: 10.3390/e21040431. Entropy (Basel). 2019. PMID: 33267145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress of Aluminum Alloy Welding/Plastic Deformation Composite Forming Technology in Achieving High-Strength Joints.Materials (Basel). 2023 Dec 15;16(24):7672. doi: 10.3390/ma16247672. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38138812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li X, Zheng C, Yin K, Cai J, Rosenthal RJ. Application of laparoscopic compression anastomosis clip for laparoscopic gastrointestinal anastomosis. Chin. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008;11(3):228230. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

