Specific CD4+ T cell phenotypes associate with bacterial control in people who 'resist' infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 38997431
- PMCID: PMC11291275
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01897-8
Specific CD4+ T cell phenotypes associate with bacterial control in people who 'resist' infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Specific CD4+ T cell phenotypes associate with bacterial control in people who 'resist' infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Nat Immunol. 2024 Oct;25(10):1976. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01959-x. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39160374 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
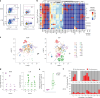
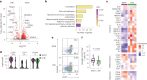
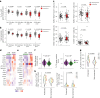
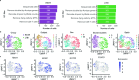
A subset of individuals exposed to Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) that we refer to as 'resisters' (RSTR) show evidence of IFN-γ- T cell responses to Mtb-specific antigens despite serially negative results on clinical testing. Here we found that Mtb-specific T cells in RSTR were clonally expanded, confirming the priming of adaptive immune responses following Mtb exposure. RSTR CD4+ T cells showed enrichment of TH17 and regulatory T cell-like functional programs compared to Mtb-specific T cells from individuals with latent Mtb infection. Using public datasets, we showed that these TH17 cell-like functional programs were associated with lack of progression to active tuberculosis among South African adolescents with latent Mtb infection and with bacterial control in nonhuman primates. Our findings suggested that RSTR may successfully control Mtb following exposure and immune priming and established a set of T cell biomarkers to facilitate further study of this clinical phenotype.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- OPP1113682/Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation)
- R01 AI125189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124348/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI137310/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93019C00071/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI115642/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057229/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- OPP1151836/Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation)
- R01 AI146072/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI153559/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- OPP1109001/Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

