Template-independent enzymatic synthesis of RNA oligonucleotides
- PMID: 38997579
- PMCID: PMC12084152
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-024-02244-w
Template-independent enzymatic synthesis of RNA oligonucleotides
Abstract
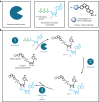
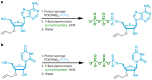
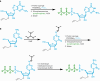
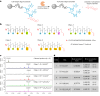
RNA oligonucleotides have emerged as a powerful therapeutic modality to treat disease, yet current manufacturing methods may not be able to deliver on anticipated future demand. Here, we report the development and optimization of an aqueous-based, template-independent enzymatic RNA oligonucleotide synthesis platform as an alternative to traditional chemical methods. The enzymatic synthesis of RNA oligonucleotides is made possible by controlled incorporation of reversible terminator nucleotides with a common 3'-O-allyl ether blocking group using new CID1 poly(U) polymerase mutant variants. We achieved an average coupling efficiency of 95% and demonstrated ten full cycles of liquid phase synthesis to produce natural and therapeutically relevant modified sequences. We then qualitatively assessed the platform on a solid phase, performing enzymatic synthesis of several N + 5 oligonucleotides on a controlled-pore glass support. Adoption of an aqueous-based process will offer key advantages including the reduction of solvent use and sustainable therapeutic oligonucleotide manufacturing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: D.J.W., J.R., E.K., N.C. and G.M.C. are inventors on a patent application (WO2020077227A3) filed by Harvard University related to this work. D.J.W., J.R., E.M., H.L., D.A., D.R. and G.M.C. hold equity in EnPlusOne Biosciences, Inc., which holds an exclusive worldwide license to the intellectual property filed by Harvard University. D.J.W., J.R., E.M., D.A., Z.Y. and D.R. were employed by EnPlusOne Biosciences, Inc., during this study, which provided internal funding to support final data collection, analysis and preparation of the manuscript. For a complete list of G.M.C.’s financial interests, please visit http://arep.med.harvard.edu/gmc/tech.html .
Figures



References
-
- Usman, N., Ogilvie, K. K., Jiang, M. Y. & Cedergren, R. J. The automated chemical synthesis of long oligoribuncleotides using 2′-O-silylated ribonucleoside 3′-O-phosphoramidites on a controlled-pore glass support: synthesis of a 43-nucleotide sequence similar to the 3′-half molecule of an Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc.109, 7845–7854 (1987). - DOI
-
- Beaucage, S. L. & Iyer, R. P. The synthesis of modified oligonucleotides by the phosphoramidite approach and their applications. Tetrahedron49, 6123–6194 (1993). - DOI
-
- Beaucage, S. L. Solid-phase synthesis of siRNA oligonucleotides. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel.11, 203–216 (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

