Analyzing the molecular mechanism of Scutellaria Radix in the treatment of sepsis using RNA sequencing
- PMID: 38997656
- PMCID: PMC11241924
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09589-2
Analyzing the molecular mechanism of Scutellaria Radix in the treatment of sepsis using RNA sequencing
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction, which seriously threatens human health. The clinical and experimental results have confirmed that Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), such as Scutellariae Radix, has anti-inflammatory effects. This provides a new idea for the treatment of sepsis. This study systematically analyzed the mechanism of Scutellariae Radix treatment in sepsis based on network pharmacology, RNA sequencing and molecular docking.
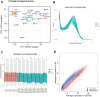
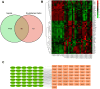
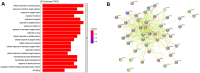
Methods: Gene expression analysis was performed using Bulk RNA sequencing on sepsis patients and healthy volunteers. After quality control of the results, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were analyzed. The active ingredients and targets of Scutellariae Radix were identified using The Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP). Gene Ontology (GO) and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) analysis were performed for disease-drug intersection targets. With the help of GEO database, Survival analysis and Meta-analysis was performed on the cross-targets to evaluate the prognostic value and screen the core targets. Subsequently, single-cell RNA sequencing was used to determine where the core targets are located within the cell. Finally, in this study, molecular docking experiments were performed to further clarify the interrelationship between the active components of Scutellariae Radix and the corresponding targets.
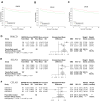
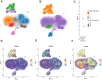
Results: There were 72 active ingredients of Scutellariae Radix, and 50 common targets of drug and disease. GO and PPI analysis showed that the intersection targets were mainly involved in response to chemical stress, response to oxygen levels, response to drug, regulation of immune system process. Survival analysis showed that PRKCD, EGLN1 and CFLAR were positively correlated with sepsis prognosis. Meta-analysis found that the three genes were highly expressed in sepsis survivor, while lowly in non-survivor. PRKCD was mostly found in Macrophages, while EGLN1 and CFLAR were widely expressed in immune cells. The active ingredient Apigenin regulates CFLAR expression, Baicalein regulates EGLN1 expression, and Wogonin regulates PRKCD expression. Molecular docking studies confrmed that the three active components of astragalus have good binding activities with their corresponding targets.
Conclusions: Apigenin, Baicalein and Wogonin, important active components of Scutellaria Radix, produce anti-sepsis effects by regulating the expression of their targets CFLAR, EGLN1 and PRKCD.
Keywords: Molecular docking; Network pharmacology; RNA sequencing; Scutellariae Radix; Sepsis; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, et al. The Third International Consensus definitions for Sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3) Jama-journal Am Med Association. 2016;315(8):801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

