Biochemical characterisation and production kinetics of high molecular-weight (HMW) putative antibacterial proteins of insect pathogenic Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates
- PMID: 38997685
- PMCID: PMC11245835
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-024-03340-2
Biochemical characterisation and production kinetics of high molecular-weight (HMW) putative antibacterial proteins of insect pathogenic Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates
Abstract
Background: Bacterial genomes often encode structures similar to phage capsids (encapsulins) and phage tails which can be induced spontaneously or using genotoxic compounds such as mitomycin C. These high molecular-weight (HMW) putative antibacterial proteins (ABPs) are used against the competitive strains under natural environment. Previously, it was unknown whether these HMW putative ABPs originating from the insect pathogenic Gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus (Bl) isolates (1821L, 1951) are spontaneously induced during the growth and pose a detrimental effect on their own survival. Furthermore, no prior work has been undertaken to determine their biochemical characteristics.
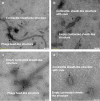
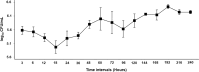
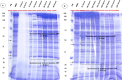
Results: Using a soft agar overlay method with polyethylene glycol precipitation, a narrow spectrum of bioactivity was found from the precipitated lysate of Bl 1951. Electron micrographs of mitomycin C- induced filtrates showed structures similar to phage capsids and contractile tails. Bioactivity assays of cell free supernatants (CFS) extracted during the growth of Bl 1821L and Bl 1951 suggested spontaneous induction of these HMW putative ABPs with an autocidal activity. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of spontaneously induced putative ABPs showed appearance of ~ 30 kDa and ~ 48 kDa bands of varying intensity across all the time intervals during the bacterial growth except in the initial hours. Statistically, spontaneously induced HMW putative ABPs of Bl 1951 exhibited a significant decrease in the number of viable cells of its producer strain after 18 h of growth in liquid. In addition, a significant change in pH and prominent bioactivity of the CFS of this particular time period was noted. Biochemically, the filtered supernatant derived from either Bl 1821L or Bl 1951 maintained bioactivity over a wide range of pH and temperature.
Conclusion: This study reports the spontaneous induction of HMW putative ABPs (bacteriocins) of Bl 1821L and Bl 1951 isolates during the course of growth with potential autocidal activity which is critically important during production as a potential biopesticide. A narrow spectrum of putative antibacterial activity of Bl 1951 precipitate was found. The stability of HMW putative ABPs of Bl 1821L and Bl 1951 over a wide range of pH and temperature can be useful in expanding the potential of this useful bacterium beyond the insecticidal value.
Keywords: Brevibacillus laterosporus; Antibacterial proteins; Biochemical characterisation; High molecular-weight; Insect pathogenic isolates; Production kinetics; Spontaneous induction.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Isolation, Purification, and Characterisation of a Phage Tail-Like Bacteriocin from the Insect Pathogenic Bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 20;12(8):1154. doi: 10.3390/biom12081154. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36009048 Free PMC article.
-
Linocin M18 protein from the insect pathogenic bacterium Brevibacillus laterosporus isolates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(13):4337-4353. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12563-8. Epub 2023 May 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37204448 Free PMC article.
-
Brevibacillus laterosporus strains BGSP7, BGSP9 and BGSP11 isolated from silage produce broad spectrum multi-antimicrobials.PLoS One. 2019 May 10;14(5):e0216773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216773. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31075157 Free PMC article.
-
Brevibacillus laterosporus, a Pathogen of Invertebrates and a Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Species.Insects. 2013 Sep 5;4(3):476-92. doi: 10.3390/insects4030476. Insects. 2013. PMID: 26462431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brevibacillus laterosporus: A Probiotic with Important Applications in Crop and Animal Production.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 12;12(3):564. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12030564. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38543615 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Purification and expression of a novel bacteriocin, JUQZ-1, against Pseudomonas syringae pv. Actinidiae (PSA), secreted by Brevibacillus laterosporus Wq-1, isolated from the rhizosphere soil of healthy kiwifruit.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1477320. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1477320. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39839114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- d’Herelle F. Sur Le rôle Du microbe filtrant bactériophage dans la dysentérie bacillaire. C Rendus Aca Sci. 1918;167:970–2.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

