Long Non-Coding RNAs Differentially Expressed in Swine Fetuses
- PMID: 38998009
- PMCID: PMC11240794
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14131897
Long Non-Coding RNAs Differentially Expressed in Swine Fetuses
Abstract
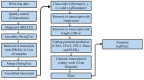
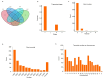
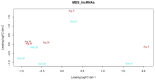
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are non-coding transcripts involved in various biological processes. The Y chromosome is known for determining the male sex in mammals. LncRNAs on the Y chromosome may play important regulatory roles. However, knowledge about their action mechanisms is still limited, especially during early fetal development. Therefore, we conducted this exploratory study aiming to identify, characterize, and investigate the differential expression of lncRNAs between male and female swine fetuses at 35 days of gestation. RNA-Seq libraries from 10 fetuses were prepared and sequenced using the Illumina platform. After sequencing, a data quality control was performed using Trimmomatic, alignment with HISAT2, and transcript assembly with StringTie. The differentially expressed lncRNAs were identified using the limma package of the R software (4.3.1). A total of 871 potentially novel lncRNAs were identified and characterized. Considering differential expression, eight lncRNAs were upregulated in male fetuses. One was mapped onto SSC12 and seven were located on the Y chromosome; among them, one lncRNA is potentially novel. These lncRNAs are involved in diverse functions, including the regulation of gene expression and the modulation of chromosomal structure. These discoveries enable future studies on lncRNAs in the fetal stage in pigs.
Keywords: bioinformatics; chromosome Y; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Screening and functional analysis of differentially expressed long non-coding RNA in the liver of mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum during the chronic pathogenic stage].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2024 May 15;36(2):137-147. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2024076. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38857956 Chinese.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs in developmental skeletal muscle of fetal goat.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3009-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27550073 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of tissue-specific long non-coding RNA in three farm animal species.BMC Genomics. 2018 Sep 18;19(1):684. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5037-7. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30227846 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Function of Long Non-coding RNA (LncRNA) Xist.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 10;9:645647. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645647. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34178980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs in human early embryonic development and their potential in ART.Hum Reprod Update. 2016 Dec;23(1):19-40. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmw035. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Hum Reprod Update. 2016. PMID: 27655590 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

