Heat Stress Effects on Physiological and Milk Yield Traits of Lactating Holstein Friesian Crossbreds Reared in Tanga Region, Tanzania
- PMID: 38998026
- PMCID: PMC11240610
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14131914
Heat Stress Effects on Physiological and Milk Yield Traits of Lactating Holstein Friesian Crossbreds Reared in Tanga Region, Tanzania
Abstract
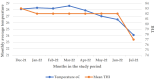
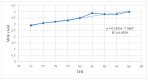
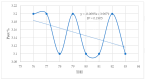
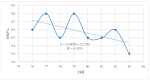
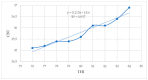
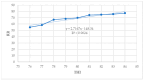
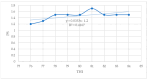
Global warming caused by climate change is a challenge for dairy farming, especially in sub-Saharan countries. Under high temperatures and relative humidity, lactating dairy cows suffer from heat stress. The objective of this study was to investigate the effects and relationship of heat stress (HS) measured by the temperature-humidity index (THI) regarding the physiological parameters and milk yield and composition of lactating Holstein Friesian crossbred dairy cows reared in the humid coastal region of Tanzania. A total of 29 lactating Holstein Friesian x Zebu crossbred dairy cows with 50% (HF50) and 75% (HF75) Holstein Friesian gene levels in the second and third months of lactation were used. The breed composition of Holstein Friesians was determined based on the animal recording system used at the Tanzania Livestock Research Institute (TALIRI), Tanga. The data collected included the daily temperature, relative humidity, daily milk yield, and physiological parameters (core body temperature, rectal temperature, respiratory rate, and panting score). THI was calculated using the equation of the National Research Council. The THI values were categorized into three classes, i.e., low THI (76-78), moderate THI (79-81), and high THI (82-84). The effects of THI on the physiological parameters and milk yield and composition were assessed. The effects of the genotype, the parity, the lactation month, and the interaction of these parameters with THI on the milk yield, milk composition, and physiological parameters were also investigated. The results show that THI and its interaction with genotypes, parity, and the lactation month had a highly significant effect on all parameters. THI influenced (p ˂ 0.05) the average daily milk yield and milk fat %, protein %, lactose %, and solids-not-fat %. As the THI increased from moderate to high levels, the average daily milk yield declined from 3.49 ± 0.04 to 3.43 ± 0.05 L/day, while the fat % increased from 2.66 ± 0.05% to 3.04 ± 0.06% and the protein decreased from 3.15 ± 0.02% to 3.13 ± 0.03%. No decline in lactose % was observed, while the solid-not-fat % declined from 8.56 ± 0.08% to 8.55 ± 0.10% as the THI values increased from moderate to high. Also, the THI influenced physiological parameters (p ˂ 0.05). The core body temperature (CBT), rectal temperature (RT), respiratory rate (RR) and panting score (PS) increased from 35.60 ± 0.01 to 36.00 ± 0.01 °C, 38.03 ± 0.02 to 38.30 ± 0.02 °C, 62.53 ± 0.29 to 72.35 ± 0.28 breaths/min, and 1.35 ± 0.01 to 1.47 ± 0.09, respectively, as the THI increased from low to high. The THI showed a weak positive correlation with the average daily milk yield and fat percentage, whereas the protein, lactose, and solids-not-fat percentages showed negative relationships with THI (p ≤ 0.05). CBT, RT, RR, and PS showed positive relationships (p ≤ 0.05) with THI. These negative relationships indicate that there is an antagonistic correlation between sensitivity to HS and the level of production. It is concluded that the THI, the genotype, the parity, and the lactation month, along with their interactions with THI, significantly influenced the milk yield, milk composition, and physiological parameters of lactating Holstein Friesian dairy crosses at THI thresholds ranging from 77 to 84.
Keywords: lactating Holstein Friesian crossbreds; milk composition; milk yield; physiological parameters; temperature–humidity index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effects of cow-related factors on rectal temperature, respiration rate, and temperature-humidity index thresholds for lactating cows exposed to heat stress.J Therm Biol. 2021 Aug;100:103041. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.103041. Epub 2021 Jun 27. J Therm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34503788
-
Genetic effects of heat stress on milk yield of Thai Holstein crossbreds.J Dairy Sci. 2011 Jan;94(1):487-92. doi: 10.3168/jds.2010-3421. J Dairy Sci. 2011. PMID: 21183060
-
Stage-specific milk yield losses and associated sweating, respiration, and rectal temperature responses under varying temperature-humidity index thresholds in lactating and dry cows.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Feb;108(2):2023-2035. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25392. Epub 2024 Nov 8. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 39521426
-
An Appropriate Genetic Approach for Improving Reproductive Traits in Crossbred Thai-Holstein Cattle under Heat Stress Conditions.Vet Sci. 2022 Mar 28;9(4):163. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9040163. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35448661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genes and models for estimating genetic parameters for heat tolerance in dairy cattle.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 27;14:1127175. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1127175. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36923799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Msalya G., Kim E.S., Laisser E.L.K., Kipanyula M.J., Karimuribo E.D., Kusiluka L.J.M., Chenyambuga S.W., Rothschild M.F. Determination of genetic structure and signatures of selection in three strains of Tanzania Shorthorn Zebu, Boran and Friesian cattle by genome-wide SNP analyses. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0171088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171088. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shija D.S., Mwai O.A., Migwi P.K., Komwihangilo D.M., Bebe B.O. Identifying Positive Deviant Farms Using Pareto-Optimality Ranking Technique to Assess Productivity and Livelihood Benefits in Smallholder Dairy Farming under Contrasting Stressful Environments in Tanzania. World. 2022;3:639–656. doi: 10.3390/world3030035. - DOI
-
- Shija D.S., Mwai O.A., Ojango J.M.K., Komwihangilo D.M., Bebe B.O. Assessing Lactation Curve Characteristics of Dairy Cows Managed under Contrasting Husbandry Practices and Stressful Environments in Tanzania. World. 2022;3:1032–1052. doi: 10.3390/world3040059. - DOI
-
- Ripkey C., Little P.D., Dominguez-salas P., Kinabo J., Mwanri A., Webb A. Increased climate variability and sedentarization in Tanzania: Health and nutrition implications on pastoral communities of Mvomero and Handeni districts, Tanzania. Glob. Food Secur. 2021;29:100516. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2021.100516. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

