Unraveling the Physicochemical, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of the Honey Produced from the Fallopia japonica Plant
- PMID: 38998468
- PMCID: PMC11240986
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13131959
Unraveling the Physicochemical, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties of the Honey Produced from the Fallopia japonica Plant
Abstract
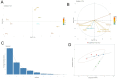
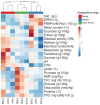
Fallopia japonica (FJ), commonly known as Japanese knotweed, is now recognized as one of the most invasive plants in Europe and globally. Despite its widespread presence in Europe and its significant nectar production, there is currently limited scientific data on the unique unifloral honey derived from it. This study examines the physicochemical composition of Fallopia japonica honey (FJH) samples collected from various regions in Romania. Additionally, the nutritional and antioxidant profiles of FJH were assessed. The sensory analysis revealed a honey with a brown-caramel color and an intense flavor, characterized by fine, consistent crystals during crystallization. The results indicated that FJH has a high carbohydrate content (fructose: 35.12-40.65 g/100 g; glucose: 28.06-37.79 g/100 g); elevated electrical conductivity (387-692 µS/cm), diastase activity (9.11-17.01 DN), and acidity (21.61-42.89 meq/kg); and substantial total phenolic (89.87-120.08 mg/100 g) and flavonoid (18.13-39.38 mg/g) contents. These findings highlight FJH's favorable nutritional properties, aligning with the standard codex for honey. The antioxidant profile of FJH demonstrated strong DPPH and ferric reduction antioxidant power (FRAP) activities, comparable to those of buckwheat honey, underscoring its potential health benefits and commercial value. These results provide new insights into how this invasive plant can be harnessed as a valuable resource for sustainable beekeeping practices.
Keywords: Fallopia japonica honey; antioxidant capacity; nutritional benefits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the Main Macro-, Micro- and Trace Elements Found in Fallopia japonica Plants and Their Traceability in Its Honey: A Case Study from the Northwestern and Western Part of Romania.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;13(3):428. doi: 10.3390/plants13030428. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337961 Free PMC article.
-
New Approaches on Japanese Knotweed (Fallopia japonica) Bioactive Compounds and Their Potential of Pharmacological and Beekeeping Activities: Challenges and Future Directions.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 29;10(12):2621. doi: 10.3390/plants10122621. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preliminary Identification and Quantification of Individual Polyphenols in Fallopia japonica Plants and Honey and Their Influence on Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activities.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;13(13):1883. doi: 10.3390/plants13131883. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999722 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Rare Himalayan Balsam (Impatiens glandulifera Royle) Honey from Croatia.Foods. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):3025. doi: 10.3390/foods11193025. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230102 Free PMC article.
-
Botanical Origin Influence on Some Honey Physicochemical Characteristics and Antioxidant Properties.Foods. 2023 May 25;12(11):2134. doi: 10.3390/foods12112134. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37297382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cucu A.A., Baci G.M., Moise A.R., Dezsi Ş., Marc B.D., Stângaciu Ş., Dezmirean D.S. Towards a Better Understanding of Nutritional and Therapeutic Effects of Honey and Their Applications in Apitherapy. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:4190. doi: 10.3390/app11094190. - DOI
-
- Hernanz D., Jara-Palacios M.J., Santos J.L., Gómez Pajuelo A., Heredia F.J., Terrab A. The Profile of Phenolic Compounds by HPLC-MS in Spanish Oak (Quercus) Honeydew Honey and Their Relationships with Color and Antioxidant Activity. LWT. 2023;180:114724. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114724. - DOI
-
- Wang L., Ning F., Liu T., Huang X., Zhang J., Liu Y., Wu D., Luo L. Physicochemical Properties, Chemical Composition, and Antioxidant Activity of Dendropanax Dentiger Honey. LWT. 2021;147:111693. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111693. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

