Comparison of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Found in Young and Mature Rhizomes
- PMID: 38998515
- PMCID: PMC11240938
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13132010
Comparison of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Found in Young and Mature Rhizomes
Abstract
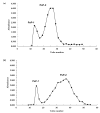
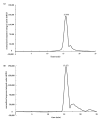
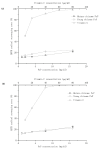
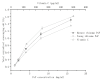
The main active component of Polygonatum sibiricum (P. sibiricum) rhizome is Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide (PsP) with antioxidant function. At present, only the mature rhizome of P. sibiricum is used to extract PsP, while the young rhizome of by-product is discarded directly as waste, resulting in significant wastage of P. sibiricum resources. We used ultrasound-assisted extraction-deep eutectic solvents (UAE-DESs) method to extract PsP of young and mature rhizomes, respectively. The extraction rate, structure composition and antioxidant ability of PsP between young and mature rhizomes were compared, so as to provide references for comprehensive utilization of P. sibiricum resources. The PsP extraction rate (33.88 ± 1.95%) of young rhizome was close to that (45.08 ± 1.92%) of mature rhizomes. The main component (PsP-2) of the PsP in young rhizome contained six kinds of monosaccharides, which belonged to acidic polysaccharides. The above characteristics of the PsP of young rhizome were similar to those of mature rhizome. The PsP of young rhizome also exhibited similar biological activity to that of the mature rhizome, which indicated even more advantages in DPPH free radical scavenging ability. The results of this study support the utility of the young rhizome, consequently helping to avoid unnecessary waste and provide reference for comprehensive utilization of P. sibiricum.
Keywords: antioxidant function; by-products; extraction rate; structure composition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
- No.2020YFC2006300/Technology from Active Health and Aging Technologic Solutions Major Project of National Key R& D Program
- No.131031107000210002/National financial projects (Public Health Emergency Project-Nutrition Health and Healthy Diet Campaign and Study of Diet and Nutrition Assessment and Intervention
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

