Enzyme Cascade Amplification-Based Immunoassay Using Alkaline Phosphatase-Linked Single-Chain Variable Fragment Fusion Tracer and MnO2 Nanosheets for Detection of Deoxynivalenol in Corn Samples
- PMID: 38998516
- PMCID: PMC11241725
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13132009
Enzyme Cascade Amplification-Based Immunoassay Using Alkaline Phosphatase-Linked Single-Chain Variable Fragment Fusion Tracer and MnO2 Nanosheets for Detection of Deoxynivalenol in Corn Samples
Abstract
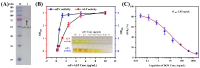
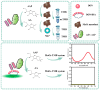
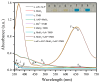
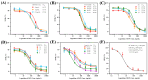
Deoxynivalenol (DON) is a common mycotoxin that contaminates cereals. Therefore, the development of sensitive and efficient detection methods for DON is essential to guarantee food safety and human health. In this study, an enzyme cascade amplification-based immunoassay (ECAIA) using a dual-functional alkaline phosphatase-linked single-chain fragment variable fusion tracer (scFv-ALP) and MnO2 nanosheets was established for DON detection. The scFv-ALP effectively catalyzes the hydrolysis of ascorbyl-2-phosphate (AAP) to produce ascorbic acid (AA). This AA subsequently interacts with MnO2 nanosheets to initiate a redox reaction that results in the loss of oxidizing properties of MnO2. In the absence of ALP, MnO2 nanosheets can oxidize 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to produce the blue oxidized product of TMB, which exhibits a signal at a wavelength of 650 nm for quantitative analysis. After optimization, the ECAIA had a limit of detection of 0.45 ng/mL and a linear range of 1.2-35.41 ng/mL. The ECAIA exhibited good accuracy in recovery experiments and high selectivity for DON. Moreover, the detection results of the actual corn samples correlated well with those from high-performance liquid chromatography. Overall, the proposed ECAIA based on the scFv-ALP and MnO2 nanosheets was demonstrated as a reliable tool for the detection of DON in corn samples.
Keywords: MnO2 nanosheets; alkaline phosphatase; cereal; immunoassay; mycotoxin; single-chain fragment variable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation of a nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion and its application in an enzyme cascade-amplified immunoassay for colorimetric detection of alpha fetoprotein in human serum.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 Dec 5;262:120088. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120088. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 34167066
-
Development of alkaline phosphatase-linked single-chain variable fragment fusion proteins for one-step immunodetection of deoxynivalenol in cereals.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 May;416(12):2929-2939. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05241-9. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38491149
-
Enzyme cascade-amplified immunoassay based on the nanobody-alkaline phosphatase fusion and MnO2 nanosheets for the detection of ochratoxin A in coffee.RSC Adv. 2021 Jun 21;11(35):21760-21766. doi: 10.1039/d1ra03615g. eCollection 2021 Jun 15. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35478809 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone-enabled colorimetric immunoassay for deoxynivalenol based on Mn2+-mediated aggregation of AuNPs.Anal Biochem. 2024 Sep;692:115572. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2024.115572. Epub 2024 May 20. Anal Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38777290
-
MnO2 nanosheets as oxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of alkaline phosphatase activity.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jun 10;186(7):408. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3519-1. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31183571
References
-
- Gab-Allah M.A., Tahoun I.F., Yamani R.N., Rend E.A., Shehata A.B. Natural occurrence of deoxynivalenol, nivalenol and deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in cereal-derived products from Egypt. Food Control. 2022;137:108974–108982. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.108974. - DOI
-
- Chen C., Turna N.S., Wu F. Risk assessment of dietary deoxynivalenol exposure in wheat products worldwide: Are new codex DON guidelines adequately protective? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019;89:11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.05.002. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

