Analysis of the Effects of Microwave Combined Induction Heating on Steamed Pork with Rice Powder
- PMID: 38998532
- PMCID: PMC11241582
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13132026
Analysis of the Effects of Microwave Combined Induction Heating on Steamed Pork with Rice Powder
Abstract
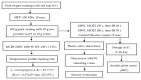
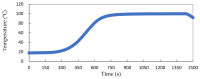
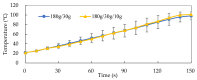
This study investigates the application of microwave combined induction heating (MCIH) to steam ready-to-eat pork with rice powder, emphasizing the advantages of rapid and uniform heating. The experimental setup included a mixture of 180 g pork strips, 30 g rice powder, and 10 g water in a CPET tray using MCIH with 1080 W microwave (MW) and 130 °C induction heating (IH) for 150 s. The results showed a quick temperature increase rate of 0.56 °C/s that achieved pasteurization against a variety of pathogenic bacteria, such as Listeria monocytogenes, but not Clostridium botulinum, by lethality calculation. Compared to typical electric cooker steaming, MCIH significantly shortened cooking time (8.6 times faster). To address rice starch gelatinization, two-stage heating techniques to steam pork with rice powder were MCIH: 150 s, and then IH: 60 s (MW1), and MCIH: 180 s, and then IH: 30 s (MW2), with no significant differences seen in color or the nine-point taste scale between treatment groups. MCIH groups had smaller shear forces than control. After MCIH cooking, no microbial counts were detected in the MW1 and MW2 groups initially, and the pork with rice powder had a shelf life of 14 days at 4 °C based on aerobic plate count assay.
Keywords: lethality; microwave combined induction heating; quality; steamed pork.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Auksornsri T., Songsermpong S. Lethality and quality evaluation of in-packaged ready-to-eat cooked Jasmine rice subjected to industrial continuous microwave pasteurization. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017;20:1856–1865. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2016.1222542. - DOI
-
- Tang J., Hong Y.-K., Inanoglu S., Liu F. Microwave pasteurization for ready-to-eat meals. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018;23:133–141. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2018.10.004. - DOI
-
- Bhunia K., Tang J., Sablani S.S. Microwave-based sustainable in-container thermal pasteurization and sterilization technologies for foods. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024. Advance Article . - DOI
-
- Bolton D., McMahon C., Doherty A., Sheridan J., McDowell D., Blair I., Harrington D. Thermal inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Yersinia enterocolitica in minced beef under laboratory conditions and in sous-vide prepared minced and solid beef cooked in a commercial retort. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000;88:626–632. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01001.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang I.-P.D., Yousef A.E., Marth E.H., Matthews M.E. Thermal inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in chicken gravy. J. Food Prot. 1992;55:492–496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

