Comparative Analysis of Texture Characteristics, Sensory Properties, and Volatile Components in Four Types of Marinated Tofu
- PMID: 38998575
- PMCID: PMC11241478
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13132068
Comparative Analysis of Texture Characteristics, Sensory Properties, and Volatile Components in Four Types of Marinated Tofu
Abstract
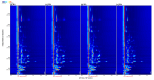
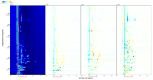
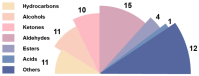
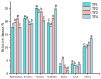
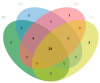
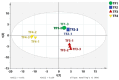
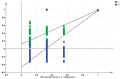
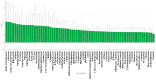
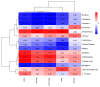
In this study, three different brands of commercially available marinated tofu were analyzed and compared with homemade products to explore the effect of key flavor substances on their sensory quality, sensory properties, texture characteristics, and volatile components. The texture characteristics and flavor substances of the three brands of commercially available marinated tofu were significantly different from those of homemade products. A total of 64 volatile components were identified by headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (HS-GC-IMS), mainly including 11 hydrocarbons, 11 alcohols, 10 ketones, 15 aldehydes, 4 esters, 1 acid, and 12 other volatile substances. Among these, nine key flavor compounds (ROAV > 1, VIP > 1) were identified using the relative odor activity value (ROAV) combined with a partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and variable importance in projection, including α-Pinene, β-Myrcene, α-Phellandrene, 1-Penten-3-one, Butanal, 3-Methyl butanal, acetic acid ethyl ester, 1,8-Cineol, and 2-Pentyl furan. The correlation heatmap showed that sensory evaluation was positively correlated with hardness, gumminess, chewiness, and springiness while negatively correlated with 2-Pentyl furan, α-Pinene, resilience, α-Phellandrene, 1-Penten-3-one, acetic acid ethyl ester, and 1,8-Cineol. Overall, this study provides a theoretical reference for developing new instant marinated tofu snacks.
Keywords: HS-GC-IMS; PLS-DA; ROAV; key volatile flavor substance; marinated tofu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
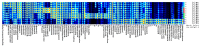
References
-
- Raja J., Punoo H.A., Masoodi F.A. Comparative study of soy paneer prepared from soymilk, blends of soymilk and skimmed milk. J. Food Process. Technol. 2014;5:1–5.
-
- Hendrich S. Nutritional, nutraceutical and functional properties of soybeans. Food Sci. Hum. Nutr. 2017;2:162.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

