Evaluation of Simultaneous Growth of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., and Listeria monocytogenes in Ground Beef Samples in Different Growth Media
- PMID: 38998601
- PMCID: PMC11240903
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13132095
Evaluation of Simultaneous Growth of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., and Listeria monocytogenes in Ground Beef Samples in Different Growth Media
Abstract
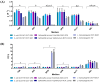
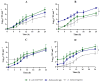
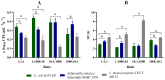
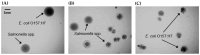
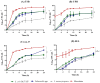
Several multiplex approaches for the simultaneous detection of pathogens in food have been developed in recent years, but the use of a single enrichment medium remains a problem. In this study, six enrichment broths (five non-selective media, tryptic soy broth (TSB), brain heart infusion broth (BHI), buffered peptone water (BPW), universal pre-enrichment broth (UPB), no. 17 broth, and a selective, Salmonella Escherichia Listeria broth (SEL)), were studied for the simultaneous detection of E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., and L. monocytogenes, to validate the suitable enrichment broth to be used for the detection methods. Different ratios of E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., and L. monocytogenes were used. Almost all non-selective broths evaluated in this study showed similar growth parameters and profiles among each other. The only selective enrichment broth under analysis (SEL) showed distinct growth features compared to the non-selective media, allowing for a slower but balanced growth of the three pathogens, which could be beneficial in preventing the overgrowth of fast-growing bacteria. In addition, when tested in ground beef samples, SEL broth seems to be the most distinctive medium with a balanced growth pattern observed for the three pathogens. Overall, this study is intended to provide the basis for the selection of suitable enrichment broths according to the technology detection to be used, the desired time of enrichment, and the expected balanced concentration of pathogens.
Keywords: culture media comparison; foodborne pathogens; growth media; pathogen detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

