Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Brassica napus L. Seeds via HPTLC, LC-QToF, and Anatomical Investigation
- PMID: 38998918
- PMCID: PMC11243287
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29132965
Comprehensive Quality Assessment of Brassica napus L. Seeds via HPTLC, LC-QToF, and Anatomical Investigation
Abstract
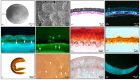
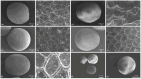
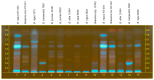
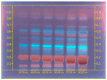
The Brassicaceae family, commonly referred to as cruciferous plants, is globally cultivated and consumed, with the Brassica genus being particularly renowned for its functional components. These vegetables are rich sources of nutrients and health-promoting phytochemicals, garnering increased attention in recent years. This study presents a comprehensive microscopic, chromatographic, and spectroscopic characterization of Brassica napus L. seeds from Kazakhstan aimed at elucidating their morphological features and chemical composition. Microscopic analysis revealed distinct localization of flavonoids, total lipids, and alkaloids. High-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) analysis of seed extracts demonstrated a complex chemical profile with significant quantities of non-polar compounds in the hexane extracts. Additionally, methanolic extracts revealed the presence of diverse chemical compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and glucosinolates. The chemical composition exhibited varietal differences across different Brassica species, with B. napus L. seeds showing higher concentrations of bioactive compounds. Furthermore, liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QToF-MS) analysis provided insights into the chemical composition, with sinapine isomers, feruloyl, and sinapoyl choline derivatives as major compounds in the seeds. This study contributes to a better understanding of the chemical diversity and quality control methods' approximations of B. napus L. seeds, highlighting their importance in functional food and nutraceutical applications.
Keywords: Brassicaceae; flavonoids; histochemistry; microscopy; phytochemistry; quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolome classification of Brassica napus L. organs via UPLC-QTOF-PDA-MS and their anti-oxidant potential.Phytochem Anal. 2013 May-Jun;24(3):277-87. doi: 10.1002/pca.2408. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Phytochem Anal. 2013. PMID: 23055344
-
Chemical profiling and separation of bioactive secondary metabolites in Maca (Lepidium peruvianum) by normal and reverse phase thin layer chromatography coupled to desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2021 Feb;56(2):e4690. doi: 10.1002/jms.4690. J Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33410238
-
Analysis of flavonoids and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in rapeseeds (Brassica napus L. var. napus) by HPLC-PDA--ESI(--)-MS(n)/HRMS.J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Apr 2;62(13):2935-45. doi: 10.1021/jf404826u. Epub 2014 Mar 25. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24620834
-
Extraction, Isolation of Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutic Potential of Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.).Molecules. 2022 Dec 12;27(24):8824. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248824. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brassica Genus Seeds: A Review on Phytochemical Screening and Pharmacological Properties.Molecules. 2022 Sep 15;27(18):6008. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186008. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Kale Extract Versus Ibuprofen After Impacted Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind Split-Mouth Clinical Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 7;16(22):3821. doi: 10.3390/nu16223821. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599607 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

