Colistin: Lights and Shadows of an Older Antibiotic
- PMID: 38998921
- PMCID: PMC11243602
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29132969
Colistin: Lights and Shadows of an Older Antibiotic
Abstract
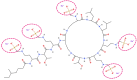
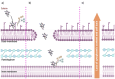
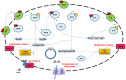
The emergence of antimicrobial resistance represents a serious threat to public health and for infections due to multidrug-resistant (MDR) microorganisms, representing one of the most important causes of death worldwide. The renewal of old antimicrobials, such as colistin, has been proposed as a valuable therapeutic alternative to the emergence of the MDR microorganisms. Although colistin is well known to present several adverse toxic effects, its usage in clinical practice has been reconsidered due to its broad spectrum of activity against Gram-negative (GN) bacteria and its important role of "last resort" agent against MDR-GN. Despite the revolutionary perspective of treatment with this old antimicrobial molecule, many questions remain open regarding the emergence of novel phenotypic traits of resistance and the optimal usage of the colistin in clinical practice. In last years, several forward steps have been made in the understanding of the resistance determinants, clinical usage, and pharmacological dosage of this molecule; however, different points regarding the role of colistin in clinical practice and the optimal pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic targets are not yet well defined. In this review, we summarize the mode of action, the emerging resistance determinants, and its optimal administration in the treatment of infections that are difficult to treat due to MDR Gram-negative bacteria.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobials; colistin; lipopeptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

