The Effects of External Interfaces on Hydrophobic Interactions I: Smooth Surface
- PMID: 38999080
- PMCID: PMC11243484
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29133128
The Effects of External Interfaces on Hydrophobic Interactions I: Smooth Surface
Abstract
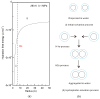
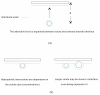
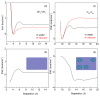
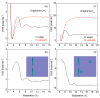
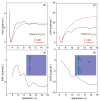
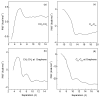
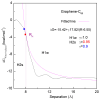
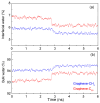
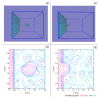
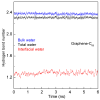
External interfaces, such as the air-water and solid-liquid interfaces, are ubiquitous in nature. Hydrophobic interactions are considered the fundamental driving force in many physical and chemical processes occurring in aqueous solutions. It is important to understand the effects of external interfaces on hydrophobic interactions. According to the structural studies on liquid water and the air-water interface, the external interface primarily affects the structure of the topmost water layer (interfacial water). Therefore, an external interface may affect hydrophobic interactions. The effects of interfaces on hydrophobicity are related not only to surface molecular polarity but also to the geometric characteristics of the external interface, such as shape and surface roughness. This study is devoted to understanding the effects of a smooth interface on hydrophobicity. Due to hydrophobic interactions, the solutes tend to accumulate at external interfaces to maximize the hydrogen bonding of water. Additionally, these can be demonstrated by the calculated potential mean forces (PMFs) using molecular dynamic (MD) simulations.
Keywords: hydrogen bonding; hydrophobic interactions; interface; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Dependence of Hydrophobic Interactions on the Shape of Solute Surface.Molecules. 2024 Jun 1;29(11):2601. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112601. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893477 Free PMC article.
-
The Hydrophobic Effects: Our Current Understanding.Molecules. 2022 Oct 18;27(20):7009. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207009. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organization of water and atmospherically relevant ions and solutes: vibrational sum frequency spectroscopy at the vapor/liquid and liquid/solid interfaces.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jan 17;45(1):110-9. doi: 10.1021/ar200152v. Epub 2011 Nov 8. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22066822
-
Recent experimental advances on hydrophobic interactions at solid/water and fluid/water interfaces.Biointerphases. 2015 Mar 15;11(1):018903. doi: 10.1116/1.4937465. Biointerphases. 2015. PMID: 26671479 Review.
-
Ions Tune Interfacial Water Structure and Modulate Hydrophobic Interactions at Silica Surfaces.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Apr 15;142(15):6991-7000. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b13273. Epub 2020 Apr 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32233477
References
-
- Morinaga A., Hasegawa K., Nomura R., Ookoshi T., Ozawa D., Goto Y., Yamada M., Naiki H. Critical role of interfaces and agitation on the nucleation of Aβ amyloid fibrils at low concentrations of Aβ monomers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1804:986–995. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

