Comparison of Three Commercially Available, AI-Driven Cephalometric Analysis Tools in Orthodontics
- PMID: 38999299
- PMCID: PMC11242750
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13133733
Comparison of Three Commercially Available, AI-Driven Cephalometric Analysis Tools in Orthodontics
Abstract
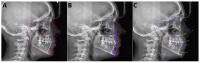
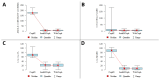
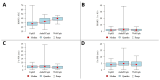
Background: Cephalometric analysis (CA) is an indispensable diagnostic tool in orthodontics for treatment planning and outcome assessment. Manual CA is time-consuming and prone to variability. Methods: This study aims to compare the accuracy and repeatability of CA results among three commercial AI-driven programs: CephX, WebCeph, and AudaxCeph. This study involved a retrospective analysis of lateral cephalograms from a single orthodontic center. Automated CA was performed using the AI programs, focusing on common parameters defined by Downs, Ricketts, and Steiner. Repeatability was tested through 50 randomly reanalyzed cases by each software. Statistical analyses included intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC3) for agreement and the Friedman test for concordance. Results: One hundred twenty-four cephalograms were analyzed. High agreement between the AI systems was noted for most parameters (ICC3 > 0.9). Notable differences were found in the measurements of angle convexity and the occlusal plane, where discrepancies suggested different methodologies among the programs. Some analyses presented high variability in the results, indicating errors. Repeatability analysis revealed perfect agreement within each program. Conclusions: AI-driven cephalometric analysis tools demonstrate a high potential for reliable and efficient orthodontic assessments, with substantial agreement in repeated analyses. Despite this, the observed discrepancies and high variability in part of analyses underscore the need for standardization across AI platforms and the critical evaluation of automated results by clinicians, particularly in parameters with significant treatment implications.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cephalometry; orthodontics; radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- McCarthy J., Minsky M.L., Rochester N., Shannon C.E. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence. AI Mag. 2006;27:12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

