Robotic-Assisted Nephrectomy for Living Kidney Donation-Single Center Initial Experience (Case Series) and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 38999324
- PMCID: PMC11242777
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13133754
Robotic-Assisted Nephrectomy for Living Kidney Donation-Single Center Initial Experience (Case Series) and Review of the Literature
Abstract
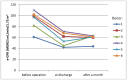
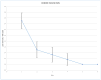
Background: Robotic-assisted nephrectomy for living kidney-donation (RANLD) has the potential of becoming the leading technique of harvesting kidney, if expertise is available. The aim of this work is to present our initial experience with robotic technique with additional hand-assistance. Materials and Methods: We initiated RANLD at our clinic using the DaVinci System in September 2022, since then harvesting six kidneys, four left and two right; in two cases, multiple arteries existed. The renal vessels were ligated using vascular staplers. All the operations included a hand-assist with the use of Gelport. The mean operation time was 119.2 min (SD 12 min). Results: There were no conversions or donors' post-operative complications. Time of discharge from the hospital was 4.5 days post-operatively. Total hospital length of stay was 7.8 days. All the harvested kidneys were transplanted, five of them with adequate function, three with initially delayed function, and one needed to be removed due to thrombotic complications. Post-operative was pain assessed on the VAS scale and overall pain was assessed according to the NRS scale. At the discharge day, donors' performance status was about 87.5% according to the Karnofsky scale. The donors resumed their normal life activity within 15.7 days and returned to work within 45.2 days. The serum mean creatinine level before the donation was 0.85 mg/dL (SD 0.1 mg/dL), and mean eGFR (MDRD) = 91.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 (SD 16.1 mL/min/1.73 m2). Conclusions: Further development of RANLD could lead to an increase in the number of living kidney donors, particularly in Poland where the number is currently lower than that of deceased donors. Prolonged operation time, longer warm ischemic time, and high equipment costs are significant drawbacks of RANLD.
Keywords: RANLD; kidney transplantation; living donor; robotic-assisted nephrectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ratner L.E., Ciseck L.J., Moore R.G., Cigarroa F.G., Kaufman H.S., Kavoussi L.R. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy. Transplantation. 1995;60:1047–1049. - PubMed
-
- Brunotte M., Rademacher S., Weber J., Sucher E., Lederer A., Hau H., Stolzenburg J., Seehofer D., Sucher R. Robotic assisted nephrectomy for living kidney donation (RANLD) with use of multiple locking clips or ligatures for renal vascular closure. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020;8:305. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.97. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous