Identification of PgRg1-3 Gene for Ginsenoside Rg1 Biosynthesis as Revealed by Combining Genome-Wide Association Study and Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis of Jilin Ginseng Core Collection
- PMID: 38999623
- PMCID: PMC11244481
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13131784
Identification of PgRg1-3 Gene for Ginsenoside Rg1 Biosynthesis as Revealed by Combining Genome-Wide Association Study and Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis of Jilin Ginseng Core Collection
Abstract
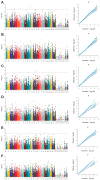
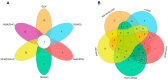
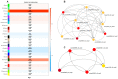
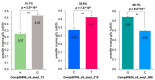
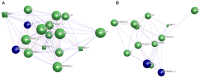
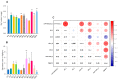
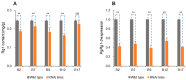
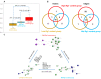
Ginseng, an important medicinal plant, is characterized by its main active component, ginsenosides. Among more than 40 ginsenosides, Rg1 is one of the ginsenosides used for measuring the quality of ginseng. Therefore, the identification and characterization of genes for Rg1 biosynthesis are important to elucidate the molecular basis of Rg1 biosynthesis. In this study, we utilized 39,327 SNPs and the corresponding Rg1 content from 344 core ginseng cultivars from Jilin Province. We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) combining weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), SNP-Rg1 content association analysis, and gene co-expression network analysis; three candidate Rg1 genes (PgRg1-1, PgRg1-2, and PgRg1-3) and one crucial candidate gene (PgRg1-3) were identified. Functional validation of PgRg1-3 was performed using methyl jasmonate (MeJA) regulation and RNAi, confirming that this gene regulates Rg1 biosynthesis. The spatial-temporal expression patterns of the PgRg1-3 gene and known key enzyme genes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis differ. Furthermore, variations in their networks have a significant impact on Rg1 biosynthesis. This study established an accurate and efficient method for identifying candidate genes, cloned a novel gene controlling Rg1 biosynthesis, and identified 73 SNPs significantly associated with Rg1 content. This provides genetic resources and effective tools for further exploring the molecular mechanisms of Rg1 biosynthesis and molecular breeding.
Keywords: Rg1 biosynthesis genes; genetic effect; genome-wide association study; ginseng; ginsenoside Rg1; weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Weighted gene co-expression network analysis and identification of ginsenoside biosynthesis candidate genes for ginseng adventitious roots under MeJA treatment.Genes Genomics. 2024 Dec;46(12):1473-1485. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01577-9. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39373827
-
Integrative transcriptome analysis identifies new oxidosqualene cyclase genes involved in ginsenoside biosynthesis in Jilin ginseng.Genomics. 2021 Jul;113(4):2304-2316. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.05.023. Epub 2021 May 25. Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34048908
-
[Identification and functional characterization of candidate genes involved in biosynthesis of ginsenoside Rg_1].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Jul;49(13):3473-3483. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20240413.101. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39041119 Chinese.
-
Hepataprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 - A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jul 12;206:178-183. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 Apr 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28427912 Review.
-
New insights into the role and mechanisms of ginsenoside Rg1 in the management of Alzheimer's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Aug;152:113207. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113207. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35667236 Review.
Cited by
-
A Fast, Efficient, and Tissue-Culture-Independent Genetic Transformation Method for Panax notoginseng and Lilium regale.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;13(17):2509. doi: 10.3390/plants13172509. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273994 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

