Early Methylglyoxal Exposure Leads to Worsened Cardiovascular Function in Young Rats
- PMID: 38999777
- PMCID: PMC11243563
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16132029
Early Methylglyoxal Exposure Leads to Worsened Cardiovascular Function in Young Rats
Abstract
Background: Though maternal diabetes effects are well described in the literature, the effects of maternal diabetes in postnatal phases are often overlooked. Diabetic individuals have higher levels of circulating glycotoxins, and there is a positive correlation between maternal-derived glycotoxins and circulating glycotoxins in their progeny. Previous studies evaluated the metabolic effects of high glycotoxin exposure during lactation in adult animals. However, here we focus on the cardiovascular system of juvenile rats.
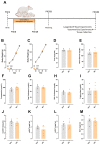
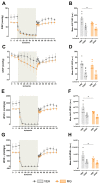
Methods: For this, we used two experimental models: 1. High Methylglyoxal (MG) environment: pregnant Wistar rats were injected with PBS (VEH group) or Methylglyoxal (MG group; 60 mg/kg/day; orally, postnatal day (PND) 3 to PND14). 2. GLO-1 inhibition: pregnant Wistar rats were injected with dimethyl sulfoxide (VEH group) or a GLO-1 inhibitor (BBGC group; 5 mg/kg/day; subcutaneously, PND1-PND5). The offspring were evaluated at PND45.
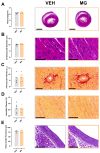
Results: MG offspring presented cardiac dysfunction and subtly worsened vasomotor responses in the presence of perivascular adipose tissue, without morphological alterations. In addition, an endogenous increase in maternal glycotoxins impacts offspring vasomotricity due to impaired redox status.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that early glycotoxin exposure led to cardiac and vascular impairments, which may increase the risk for developing cardiovascular diseases later in life.
Keywords: BBGC; glycotoxins; lactation; left ventricular dysfunction; methylglyoxal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bashir M., Dabbous Z., Baagar K., Elkhatib F., Ibrahim A., Brich S.A., Abdel-Rahman M.E., Konje J.C., Abou-Samra A.B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy: The Impact of Maternal Weight and Early Glycaemic Control on Outcomes. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2019;233:53–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.12.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UIDB//04539/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDP//04539/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- LA/P/0058/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- Finance Code 001/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- Finance Code 001/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

