Serotonin Influences Insulin Secretion in Rat Insulinoma INS-1E Cells
- PMID: 38999937
- PMCID: PMC11241493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25136828
Serotonin Influences Insulin Secretion in Rat Insulinoma INS-1E Cells
Abstract
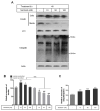
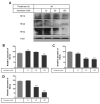
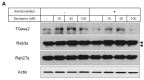
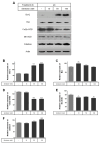
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine that plays a critical role in insulin secretion, energy metabolism, and mitochondrial biogenesis. However, the action of serotonin in insulin production and secretion by pancreatic β cells has not yet been elucidated. Here, we investigated how exogenous nanomolar serotonin concentrations regulate insulin synthesis and secretion in rat insulinoma INS-1E cells. Nanomolar serotonin concentrations (10 and 50 nM) significantly increased insulin protein expression above the constant levels in untreated control cells and decreased insulin protein levels in the media. The reductions in insulin protein levels in the media may be associated with ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. The levels of membrane vesicle trafficking-related proteins including Rab5, Rab3A, syntaxin6, clathrin, and EEA1 proteins were significantly decreased by serotonin treatment compared to the untreated control cells, whereas the expressions of Rab27A, GOPC, and p-caveolin-1 proteins were significantly reduced by serotonin treatment. In this condition, serotonin receptors, Gαq-coupled 5-HT2b receptor (Htr2b), and ligand-gated ion channel receptor Htr3a were significantly decreased by serotonin treatment. To confirm the serotonylation of Rab3A and Rab27A during insulin secretion, we investigated the protein levels of Rab3A and Rab27A, in which transglutaminase 2 (TGase2) serotonylated Rab3A but not Rab27A. The increases in ERK phosphorylation levels were consistent with increases in the expression of p-Akt. Also, the expression level of the Bcl-2 protein was significantly increased by 50 and 100 nM serotonin treatment compared to the untreated control cells, whereas the levels of Cu/Zn-SOD and Mn-SOD proteins decreased. These results indicate that nanomolar serotonin treatment regulates the insulin protein level but decreases this level in media through membrane vesicle trafficking-related proteins (Rab5, Rab3A, syntaxin6, clathrin, and EEA1), the Akt/ERK pathway, and Htr2b/Htr3a in INS-1E cells.
Keywords: Akt/ERK; insulin; serotonin; serotonin receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanomolar melatonin influences insulin synthesis and secretion in rat insulinoma INS-1E cells.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;71(5). doi: 10.26402/jpp.2020.5.10. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33571963
-
Intracellular serotonin modulates insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells by protein serotonylation.PLoS Biol. 2009 Oct;7(10):e1000229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000229. Epub 2009 Oct 27. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19859528 Free PMC article.
-
Indomethacin decreases insulin secretion by reducing KCa3.1 as a biomarker of pancreatic tumor and causes apoptotic cell death.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020 Jul;34(7):e22488. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22488. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32128977
-
Functional role of serotonin in insulin secretion in a diet-induced insulin-resistant state.Endocrinology. 2015 Feb;156(2):444-52. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1687. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25426873 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic β cell models for screening insulin secretagogues and cytotoxicity.J Appl Toxicol. 2025 Jan;45(1):89-106. doi: 10.1002/jat.4658. Epub 2024 Jun 22. J Appl Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39662958 Review.
References
-
- Nichols C., Sanders-Bush E. Serotonin receptor signaling and hallucinogenic drug action. Heffer Rev. Psychedelic Res. 2001;2:73–79.
-
- Bennet H., Balhuizen A., Medina A., Dekker Nitert M., Ottosson Laakso E., Essén S., Spégel P., Storm P., Krus U., Wierup N., et al. Altered serotonin (5-HT) 1D and 2A receptor expression may contribute to defective insulin and glucagon secretion in human type 2 diabetes. Peptides. 2015;71:113–120. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2015.07.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Falk B., Hellman B. Evidence for the presence of biogenic amines in the pancreatic islets. Experientia. 1963;19:139–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02171596. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

